News
-
 Neuroscience
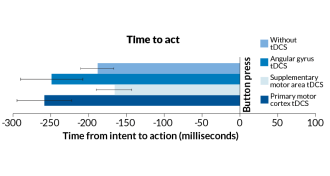
NeuroscienceStimulating nerve cells stretches time between thinking, doing
A head zap can stretch the time between intention and action.
-
 Chemistry
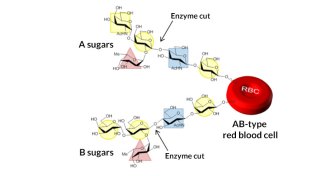
ChemistrySugar-cleaving molecule raises hope for universal blood
An engineered enzyme can quickly slice and dice some A and B markers from blood cells, bringing researchers closer to creating universal blood.
By Beth Mole -
 Genetics
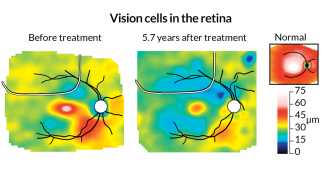
GeneticsGene therapy for blindness dims a bit
Gene therapy improves vision temporarily but can’t save sight.
-
 Neuroscience
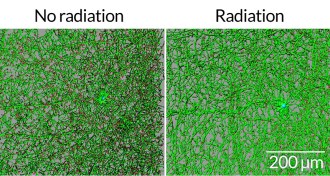
NeuroscienceZipping to Mars could badly zap brain nerve cells
Charged particles like the ones astronauts might encounter wallop the brain, mouse study suggests.
-
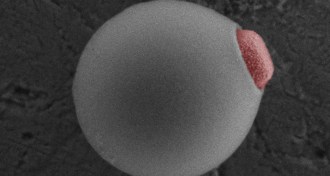 Physics
PhysicsTiny particles propel themselves upstream
Light-activated, human-made particles can align themselves with the flow of a fluid and swim upstream.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExplanation for G’s imprecision stumbles
A surprising new result seems to suggest that subtle changes in Earth’s rotation rate could account for physicists’ difficulty in measuring Newton’s gravitational constant. But some confusion with dates appears to derail the finding.
By Andrew Grant -
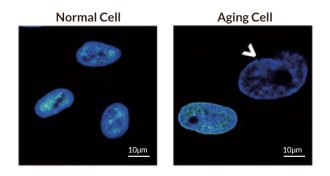 Genetics
GeneticsDNA disorganization linked to aging
Changes in the way that DNA is tightly packed in cells leads to mayhem that promotes the aging process.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis dinosaur’s ride may have been a glide
A new dino called Yi qi may have taken to the skies with wings akin to those of pterosaurs and flying squirrels.
-
 Earth
EarthCosmic rays illuminate lightning
Radio waves emitted by particles zipping through thunderstorms allow physicists to probe thunderclouds and, perhaps eventually, learn what triggers lightning strikes.
By Andrew Grant -
 Astronomy
AstronomyTiny explosions add up to heat corona
Millions of mini-explosions every second on the sun could solve the riddle of why the sun’s atmosphere is so much warmer than its surface.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyChildhood bullying leads to long-term mental health problems
U.S., British data raise bullying’s profile as a long-term mental health hazard for kids.
By Bruce Bower -
 Earth
EarthStronger quakes could strike other segments of Nepal fault
The magnitude 7.8 earthquake that struck Nepal’s capital city could be overshadowed by larger future earthquakes along the Himalayas, scientists say.