News
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsProton’s magnetic properties pinned down
A precise measurement of a proton’s magnetic properties could help reveal subtle differences between matter and antimatter.
By Andrew Grant -
 Life
LifeStarchy foods more filling than fiber, lab tests suggest
Tests of gut microbe digestion of potato starch and fiber suggest that moving away from grass-heavy ancestral diets may not be the reason for obesity epidemic.
-
 Life
LifeDrab female birds had more colorful evolution
Males weren’t the main players in evolution of sex differences in avian plumage.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomySun shines new life on Kepler space telescope
NASA approved a proposal to bring the crippled Kepler spacecraft back to life, using sunlight as balance to help the telescope search for planets and more.
-
 Psychology
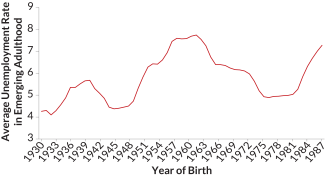
PsychologyRecessions take a lasting toll on narcissism
Coming of age in hard economic times makes people less likely to feel superior and entitled later in life.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLife span lengthens when mice feel less pain
When rodents are missing a sensory protein, their metabolism revs up and they live longer.
-
 Cosmology
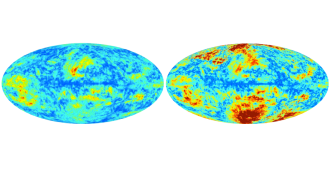
CosmologyDustup emerges over gravitational waves discovery
While cosmologists wait for data from Planck satellite, some worry that BICEP2 data actually come from our galaxy.
-
 Life
LifeIn a surprise find, placentas harbor bacteria
Mouth bacteria make their way to the placenta. Some mixes may trigger premature birth.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum cryptography could shed test for hackers
An added protection of a proposed quantum cryptography method makes eavesdropping nearly impossible.
By Andrew Grant -
 Life
LifeGenes gives clues to outcome of species interbreeding
Genetics provides clues to why hybrid river fish formed a subspecies but insects formed a new species.
-
 Climate
ClimateEnvironmental change may spur growth of ‘rock snot’
A controversial new theory suggests alga that forms rock snot isn’t an invader, but a low-key species native to many rivers.
By Beth Mole -
 Astronomy
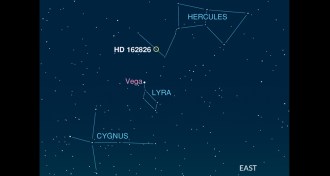
AstronomySun’s sibling spotted
A nearby star may have come from the same birth cluster as the sun; learning how to find other solar siblings could point the way to their common origin.