News
-
 Climate
ClimateEnvironmental change may spur growth of ‘rock snot’
A controversial new theory suggests alga that forms rock snot isn’t an invader, but a low-key species native to many rivers.
By Beth Mole -
 Astronomy
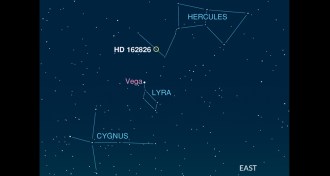
AstronomySun’s sibling spotted
A nearby star may have come from the same birth cluster as the sun; learning how to find other solar siblings could point the way to their common origin.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceRecyclable superplastics made with old chemistry
A new durable plastic and a self-healing gel are the first high-performance polymers that are easily recycled.
By Beth Mole -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyTeen’s skeleton ties New World settlers to Native Americans
Underwater cave discovery in Mexico shows genetic range of New World’s ancient Asian colonists.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyMilky Way’s far side reveals some secrets
Variable stars provide first direct measurements of distance to the far side of the Milky Way.
-
 Earth
EarthTiny earthquakes may follow groundwater loss
Draining California’s aquifers may stress San Andreas Fault, triggering earthquakes and forcing mountains to rise.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePlaying football linked to brain changes
Division I college football players have smaller hippocampi, especially if they’ve had concussions.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsNext-gen quantum teleportation in just 2 photons
Researchers teleport quantum information between two photons instead of the standard three.
By Andrew Grant -
 Oceans
OceansDeepwater Horizon methane lingered longer than thought
Microbes may not have consumed methane from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill as fast as previously thought.
-
 Neuroscience
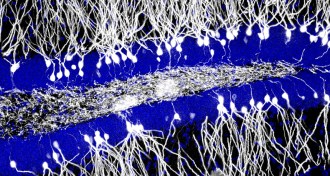
NeuroscienceBirth of new brain cells might erase babies’ memories
The growth of new neurons in early childhood may explain why adults can’t remember being infants.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Psychology
PsychologyFarming practices have shaped thinking styles
The different levels of cooperation required to grow rice and wheat have sown psychological differences within China and possibly between East Asia and the West.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsEveryday electronics may upset birds’ compass
Weak electromagnetic waves, coming from normal university activities, interfere with European robins’ migratory orientation.
By Susan Milius