Notebook
-
 Oceans
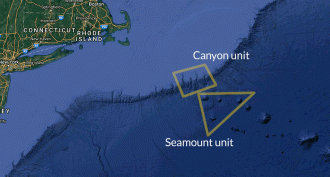
OceansFirst U.S. ocean monument named in the Atlantic
A region of ocean off the coast of Cape Cod has become the first U.S. marine national monument in the Atlantic Ocean, President Barack Obama announced.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPterosaurs weren’t all super-sized in the Late Cretaceous
A 77-million-year-old flying reptile may be the smallest pterosaur of the Late Cretaceous.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceRock star Freddie Mercury now has his own space rock
Queen front man Freddie Mercury is the latest in a long list of celebrities to have an asteroid named after him.
-
 Genetics
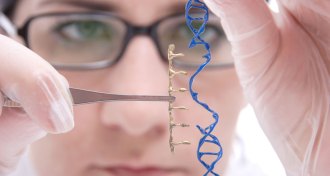
GeneticsGenetic surgery is closer to reality
A molecular scalpel called CRISPR/Cas9 has made gene editing possible.
-
 Life
LifeCalifornia’s goby is actually two different fish
One fish, two fish: California’s tidewater goby is two species.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDwarf lemurs don’t agree on sleep
Fat-tailed dwarf lemurs’ surprising hibernation-sleep doesn’t show up in ground-hibernating relatives.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyGreenland may be home to Earth’s oldest fossils
Dating to 3.7 billion years ago, mounds of sediment called stromatolites found in Greenland may be the oldest fossilized evidence of life on Earth.
-
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClean inside those bagpipes — and trumpets and clarinets
Bagpipes’ moist interiors may be the perfect breeding ground for yeasts and molds.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
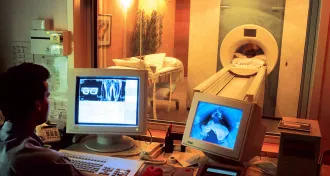
NeuroscienceComputers refine epilepsy treatment
Surgeons harnessed computers in 1966 to pinpoint source of epilepsy in the brain.
-
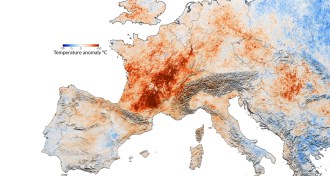 Climate
ClimateGlobal warming amplified death toll during 2003 European heat wave
Climate change caused hundreds of fatalities in London and Paris during the 2003 European heat wave, simulations suggest.
-
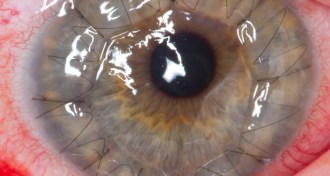 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCornea donation may have sex bias
Women receiving a corneal transplant do better when their donors are female, new research finds.
By Amber Dance