Say What?
-
 Health & Medicine
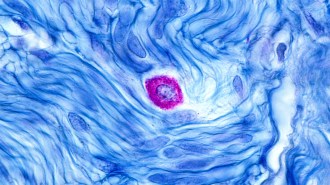
Health & MedicineDuring an allergic response, some immune cells digest others
Mast cells lure and trap other immune cells during allergic reactions, using their compounds to increase inflammation in a process dubbed nexocytosis
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThere’s a new term for attempting to own the wind: ventography
Nations established territorial claims underground to access oil and gas. Now they are expanding those claims upward to snag the wind.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Particle Physics
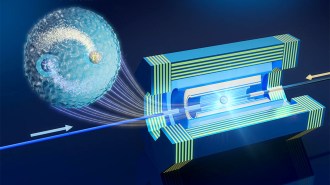
Particle PhysicsScientists propose a hunt for never-before-seen ‘tauonium’ atoms
Made of heavy relatives of the electron, the exotic atoms could be used to test the theory of quantum electrodynamics.
-
 Animals
AnimalsParrots can move along thin branches using ‘beakiation’
The movement involves swinging along the underside of branches with their beaks and feet, similar to how primates swing between trees.
-
 Earth
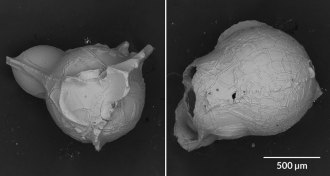
EarthThese tiny, crackly bubbles are a new type of volcanic ash
Scientists have identified a new type of volcanic ash made up of millimeter-long spheres with a crackled surface.
-
 Earth
EarthYou’re living in a new geologic age. It’s called the Meghalayan
The newly defined Meghalayan Age began at the same time as a global, climate-driven event that led to human upheavals.
By Beth Geiger -
 Health & Medicine
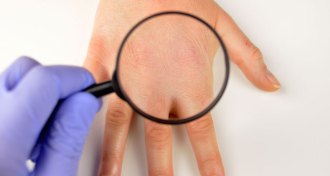
Health & MedicineDelusions of skin infestation may not be so rare
Delusional infestation, an unwavering belief that one’s skin is overrun with creatures or objects, may not be as rare as previously thought, researchers say.
-
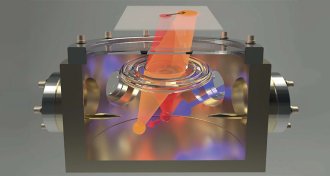 Physics
PhysicsA single atom can gauge teensy electromagnetic forces
The force of scattering particles of light was measured in zeptonewtons, a billionth of a trillionth of a newton.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis sea slug makes its prey do half the food catching
Nudibranchs’ stolen meals blur classic predator-prey levels.
By Susan Milius -
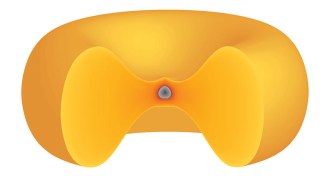 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceEarth might once have resembled a hot, steamy doughnut
Newly proposed space objects called synestias are large, spinning hunks of mostly vaporized rock. They look like a jelly-filled doughnut.
-
 Earth
EarthIce particles shaped like lollipops fall from clouds
Small ice particles called ice-lollies, because of their lollipop-like appearance, can form in clouds.
-
 Earth
Earth‘River piracy’ on a high glacier lets one waterway rob another
The melting of one of Canada’s largest glaciers has rerouted meltwater from one stream into another in an instance of river piracy.