Uncategorized
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsA new quantum engine packs more power than its standard counterparts
A new type of tiny machine harnesses quantum physics to produce more power than a normal engine, under certain conditions.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA single-dose antidote may help prevent fentanyl overdoses
Packing overdose medication into nanoparticles could help it better counteract dangerous synthetic opioids.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWatch a desert kangaroo rat drop-kick a rattlesnake
Desert kangaroo rats have a wide arsenal for dodging rattlesnake ambushes. But the most dramatic might be their powerful midair kick.
By Mike Denison -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThe first known fossil of a Denisovan skull has been found in a Siberian cave
A new fossil and evidence that the hominids interbred with humans as recently as 15,000 years ago only add to Denisovans’ mystery.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
Astronomy4 things we’ll learn from the first closeup image of a black hole
Scientists are gearing up to release the first image of the black hole at the center of the galaxy. Here’s what they hope to find out.
-
 Climate
ClimateOne Antarctic ice shelf gets half its annual snowfall in just 10 days
Antarctica’s coasts get most of their snow from just a few big storms each year.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSaturn’s rings paint some of its moons shades of blue and red
Moons located among Saturn’s inner rings are different colors depending on their distance from the planet, suggesting they’re picking up ring debris.
-
 Animals
AnimalsChytrid’s frog-killing toll has been tallied — and it’s bad
Losses due to the amphibian-killing chytrid fungus are “the greatest documented loss of biodiversity attributable to a pathogen,” researchers find.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGeneticists close in on how mosquitoes sniff out human sweat
A long-sought protein proves vital for mosquitoes’ ability to detect lactic acid, a great clue for finding a human.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, drug abuse was higher among physicians than the public
In 1969, physicians abused drugs at a higher rate than the general public — that’s still true today.
By Jeremy Rehm -
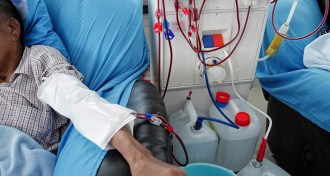 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlood vessels built from a patient’s cells could help people on dialysis
Bioengineered blood vessels could provide a safer alternative than donor vessels or synthetic implants.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTreating cystic fibrosis patients before birth could safeguard organs
Starting a cystic fibrosis drug sooner than usual may protect an afflicted child’s lungs, pancreases and reproductive tissue, a study in ferrets hints.