Uncategorized
-
 Earth
EarthOcean’s plastics offer a floating fortress to a mess of microbes
Microbes take up residence on ocean plastics, potentially causing changes in ocean environments.
-
 Agriculture
AgriculturePlants trick bacteria into attacking too soon
Scientists have discovered that a plant compound interferes with bacterial communication.
-
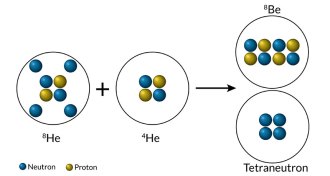 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsPhysicists find signs of four-neutron nucleus
Strong evidence of a tetraneutron, an atomic nucleus with four neutrons but no protons, defies physicists’ theoretical expectations.
By Andrew Grant -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCancer drug’s usefulness against Alzheimer’s disputed
A preliminary report questions the anti-Alzheimer’s activity of a cancer-fighting drug.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyDon’t blame winter for that bleak mood
Contrary to popular opinion, depression doesn’t spike in winter, survey finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Tech
Tech‘Rise of the Robots’ chronicles race to build disaster-relief bots
NOVA’s “Rise of the Robots” lays out the difficulties of making humanoid robots that can help out in disasters.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Tech
TechPill measures gut gas
A gas-sensing ingestible capsule tested in pigs could someday help doctors assess people’s gastrointestinal health.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhite-tailed deer have their own form of malaria
The otherwise well-studied white-tailed deer turns out to carry the first malaria parasite discovered in any deer.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsHarvester ants are restless, enigmatic architects
Florida harvester ants dig complex, curly nests over, then leave and do it again.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMouse study offers clues to brain’s response to concussions
The brain needs time to recover between head hits, a study in mice suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy some birds sing elaborate songs in the winter
Several obvious hypotheses fail to explain why great reed warblers sing in winter.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsMeet the tarantula in black
Named for Johnny Cash, a new species of tarantula makes its home in the shadow of Folsom Prison.