Uncategorized
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyQuantum spookiness, magnetic mysteries and more feedback
Letters and comments from readers on quantum spookiness, Earth's magnetic field, and more.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsAntiprotons match protons in response to strong nuclear force
The first study of how antiprotons interact with each other reveals yet again that particles of antimatter behave just like their ordinary matter counterparts.
By Andrew Grant -
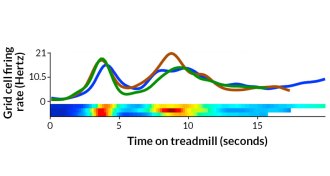 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s GPS cells map time and distance, not just location
Brain’s GPS cells map time and distance, too.
-
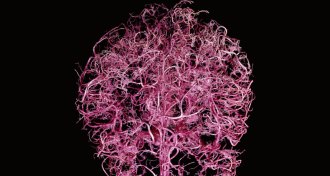 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBlood exerts a powerful influence on the brain
Instead of just responding to the energy needs of neurons, the blood can have a direct and powerful influence on the brain.
-
 Animals
AnimalsColor of light sets dung beetles straight
Dung beetles may rely on green and ultraviolet colors in the sky to help orient themselves.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient larvae built predator-thwarting mazes
Mazelike tunnels built by ancient insect larvae offered protection from predators, paleontologists propose.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDiagram captures microbes’ influence across animal kingdom
A network diagram of animal species shows that many microbes living in humans also make themselves at home in dogs, pigs and cattle.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Earth
EarthNew recipe for diamonds: Just add acid
Simulating the chemistry, pressures and temperatures in Earth’s interior, scientists have discovered a new way diamonds can form.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHunchbacked conchs jump at the smell of danger
Hunchbacked conchs are among the most vigorous of snailkind’s few jumpers.
By Susan Milius -
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘Failure’ explores errors’ upsides
Missteps are a must in science, biologist argues in new book.
By Janet Raloff -
 Climate
ClimateEocene temperature spike caused by half as much CO2 as once thought
Revised experiments demonstrate that hot temperatures during the Eocene resulted from lower carbon dioxide concentrations than previously thought.
-
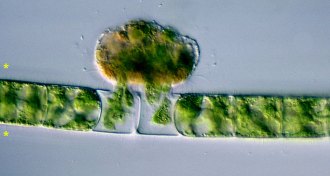 Paleontology
PaleontologyVampire microbes sucked some ancient life dry
Hole-ridden fossils suggest that vampirelike microbes were among the first predators that targeted eukaryotes.