Herminia Pasantes discovered how taurine helps brain cells regulate their size
The prevention and treatment of brain edema builds on her decades of work
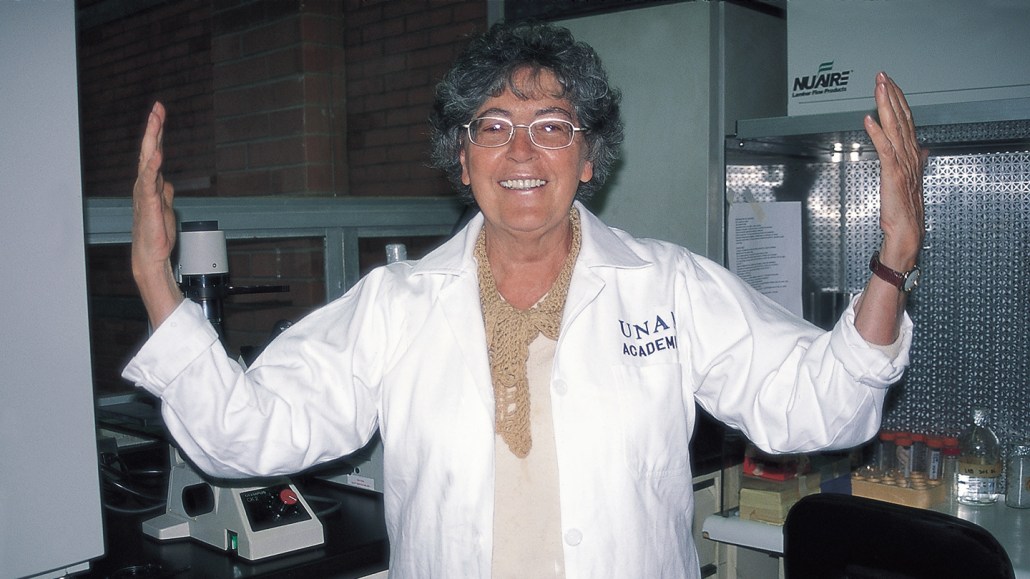

Herminia Pasantes is shown in her lab around 1990, just after results came in showing that taurine acts as an osmolyte in a type of neuron called an astrocyte.
Courtesy of H. Pasantes
When Herminia Pasantes Ordóñez was about 14 years old, in 1950, she heard her mother tell her father that she would never find a husband. Pasantes had to wear thick glasses for her poor eyesight. In her mother’s eyes, those glasses meant her future as a “good woman” was doomed. “This made my life easier,” says Pasantes, “because it was already said that I was going to study.”
At a time when it was uncommon for women to become scientists, Pasantes studied biology at the National Autonomous University of Mexico in Mexico City, or UNAM. She was the first member of her family to go to college.
She became a neurobiologist and one of the most important Mexican scientists of her time. Her studies on the role of the chemical taurine in the brain offer deep insights into how cells maintain their size — essential to proper functioning. In 2001, she became the first woman to earn Mexico’s National Prize for Sciences and Arts in the area of physical, mathematical and natural sciences.
“We basically learned about cell volume regulation through the eyes and work of Herminia,” says Alexander Mongin, a Belarusian neuroscientist at Albany Medical College in New York.
Pasantes did get married, in 1965 while doing her master’s in biochemistry at UNAM. She had a daughter in 1966 and a son in 1967 before starting a Ph.D. in natural sciences in 1970 at the Center for Neurochemistry at the University of Strasbourg in France. There, she worked in the laboratory of Paul Mandel, a Polish pioneer in neurochemistry.
The lab was trying to find out everything there was to know about the retina, the layer of tissue at the back of the eye that is sensitive to light. Pasantes decided to test whether free amino acids, a group that aren’t incorporated into proteins, were present in the retinas and brain of mice. Her first chromatography — a lab technique that lets scientists separate and identify the components of a sample — showed an immense amount of taurine in both tissues. Taurine would drive the rest of her scientific career, including work in her own lab, which she started around 1975 at the Institute of Cellular Physiology at UNAM.
Taurine turns out to be widely distributed in animal tissues and has diverse biological functions, some of which were discovered by Pasantes. Her research found that taurine helps maintain cell volume in nerve cells, and that it protects brain, muscle, heart and retinal cells by preventing the death of stem cells, which give rise to all specialized cells in the body.
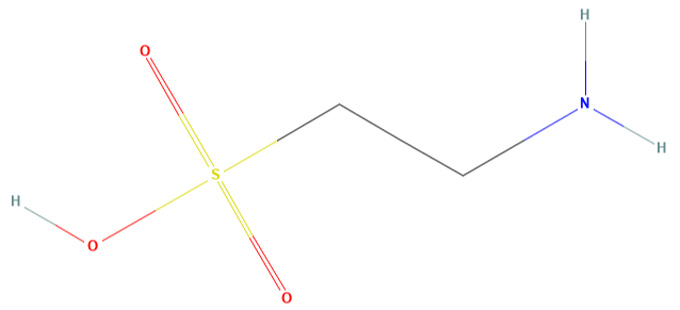
Contrary to what most scientists had believed at the time, taurine didn’t work as a neurotransmitter sending messages between nerve cells. Pasantes demonstrated for the first time that it worked as an osmolyte in the brain. Osmolytes help maintain the size and integrity of cells by opening up channels in their membranes to get water in or out.
Pasantes says she spent many years looking for an answer for why there is so much taurine in the brain. “When you ask nature a question, 80 to 90 percent of the time, it responds no,” she says. “But when it answers yes, it’s wonderful.”
Pasantes’ lab was one of the big four labs that did groundbreaking work on cell volume regulation in the brain, says Mongin.
Her work and that of others proved taurine has a protective effect; it’s the reason the chemical is today sprinkled in the containers that carry organs for transplants. Pasantes’ work was the foundation for our understanding of how to prevent and treat brain edema, a condition where the brain swells due to excessive accumulation of fluid, from head trauma or reduced blood supply, for example. She and other experts also reviewed the role of taurine for Red Bull, which added the chemical to its formula because of potentially protective effects in the heart.
Pasantes stopped doing research in 2019 and spends her time talking and writing about science. She hopes her story speaks to women around the world who wish to be scientists: “It is important to send the message that it is possible,” she says.
Years before she was accepted into Mandel’s lab, her application to a Ph.D. in biochemistry at the UNAM was rejected. Pasantes says the reason was that she had just had her daughter. Looking back, this moment was “one of the most wonderful things that could’ve happened to me,” Pasantes says, because she ended up in Strasbourg, where her potential as a researcher bloomed.
Rosa María González Victoria, a social scientist at the Autonomous University of the State of Hidalgo in Pachuca, Mexico, who specializes in gender studies, recently interviewed Pasantes for a book about Mexican women in science. González Victoria thinks Pasantes’ response to that early rejection speaks to the kind of person she is: “A woman that takes those no’s and turns them into yes’s.”