The Orion nebula, a well-known star-forming region 1,500 light-years from Earth, is rife with young, sunlike stars swaddled by disks of gas, dust, and ice. Such disks are the stuff from which planets coalesce. But Orion’s protoplanetary disks are being eroded by the harsh ultraviolet light and intense winds from a massive star within the nebula. Whether the disks can make planets in this hostile setting has remained a question since the disks were first discovered with the Hubble Space Telescope more than a decade ago.
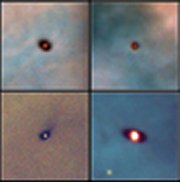
New observations with the Submillimeter Array on Hawaii’s Mauna Kea reveal that despite their bombardment, the disks in Orion have enough material—the equivalent of 10 to 20 Jupiters—to form planets.
Since most sunlike stars in the Milky Way form in severe environments similar to that of Orion, the finding suggests that planets could coalesce around many such stars in the galaxy, says David Wilner of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Mass. He and his colleagues describe their study of the Orion nebula’s protoplanetary disks in an upcoming Astrophysical Journal.