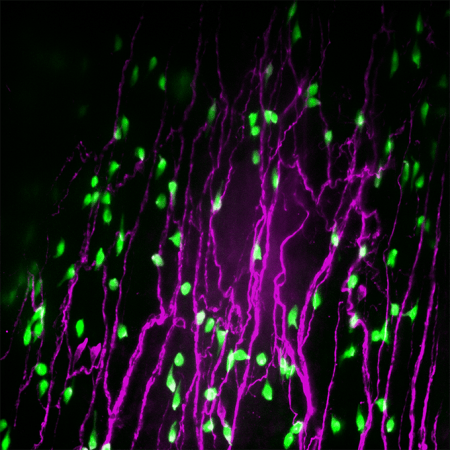
These windpipe cells trigger coughs to keep water out of the lungs
Experiments in mice show that neuroendocrine cells in the trachea react to water and acid
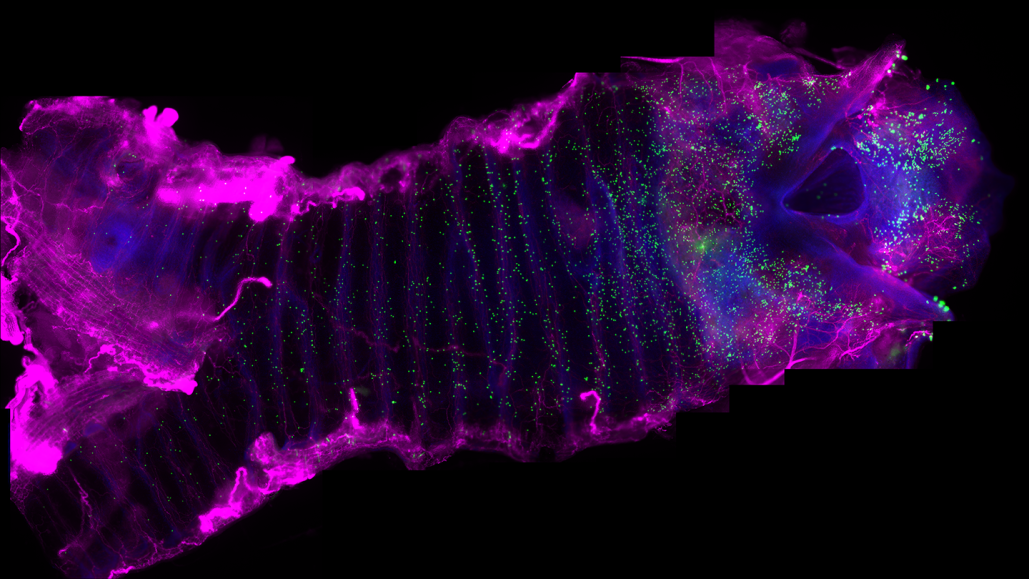
Neuroendocrine cells (green) are scattered across the trachea and larynx, as imaged in a mouse. A new study reveals how these cells communicate with cells in the nervous system (pink) to help prevent substances such as water or acid from getting into the lungs.
Laura Seeholzer