Video
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTiny treadmills show how fruit flies walk
A method to force fruit flies to move shows the insects’ stepping behavior and holds clues to other animals’ brains and movement.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceThis robot can tell when you’re about to smile — and smile back
Using machine learning, researchers trained Emo to make facial expressions in sync with humans.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEavesdropping on fish could help us keep better tabs on underwater worlds
Scientists are on a quest to log all the sounds of fish communication. The result could lead to better monitoring of ecosystems and fish behavior.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChickadees use memory ‘bar codes’ to find their hidden food stashes
Unique subsets of neurons in a chickadee’s memory center light up for each distinct cache, hinting at how episodic memories are encoded in the brain.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsBy fluttering its wings, this bird uses body language to tell its mate ‘after you’
New observations suggest that Japanese tits gesture to communicate complex messages — a rare ability in the animal kingdom and a first seen in birds.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceAI learned how to sway humans by watching a cooperative cooking game
New research used the game Overcooked to show how offline reinforcement learning algorithms could teach bots to collaborate with — or manipulate — us.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyTimbre can affect what harmony is music to our ears
The acoustic qualities of instruments may have influenced variations in musical scales and preferred harmonies.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBig monarch caterpillars don’t avoid toxic milkweed goo. They binge on it
Instead of nipping milkweed to drain the plants’ defensive sap, older monarch caterpillars may seek the toxic sap. Lab larvae guzzled it from a pipette.
By Susan Milius -
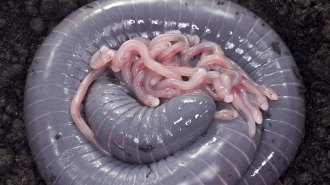 Life
LifeThis is the first egg-laying amphibian found to feed its babies ‘milk’
Similar to mammals, these ringed caecilians make a nutrient-rich milk-like fluid to feed their mewling hatchlings up to six times a day.
By Jake Buehler -
 Environment
EnvironmentHow air pollution may make it harder for pollinators to find flowers
Certain air pollutants that build up at night can break down the same fragrance molecules that attract pollinators like hawk moths to primroses.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDoes this drone image show a newborn white shark? Experts aren’t sure
If a claim of the first-ever sighting of a newborn white shark holds, it could help solve a mystery of where adult white sharks give birth.
-
 Animals
AnimalsParrots can move along thin branches using ‘beakiation’
The movement involves swinging along the underside of branches with their beaks and feet, similar to how primates swing between trees.