Animals
-
 Animals
AnimalsUsing comb-shaped teeth, Baikal seals feed on tiny crustaceans like whales do
Seals in Lake Baikal use comb-shaped teeth to catch scores of amphipods, a study finds. The diet may be behind the seals’ relative success.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsA highly contagious face cancer may not wipe out Tasmanian devils after all
Devil facial tumor disease has killed so many Tasmanian devils that it was feared they would die out. But a new analysis finds its spread is slowing.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGiant pandas may roll in horse poop to feel warm
By coating themselves in fresh horse manure, wild giant pandas may be seeking a chemical in the poop that inhibits a cold-sensing protein.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMineral body armor helps some leaf-cutting ants win fights with bigger kin
Researchers have found that at least one species of leaf-cutting ant has a tough layer of calcite on its exoskeleton.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA face mask may turn up a male wrinkle-faced bat’s sex appeal
The first-ever scientific observations of a wrinkle-faced bat’s courtship shows that, when flirting, the males raise their white furry face coverings.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsOn a cool night in Malaysia, scientists track mysterious colugos across the treetops
Our reporter tags along for nighttime observations of these elusive gliding mammals.
By Yao-Hua Law -
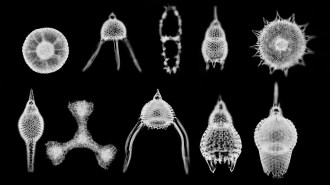 Earth
Earth50 years ago, scientists named Earth’s magnetic field as a suspect in extinctions
In 1970, researchers saw a link between magnetic pole reversals and extinctions. Fifty years later, scientists have uncovered more suggestive examples but no strong evidence of a direct link.lamb
-
 Life
LifeMonarch caterpillars head-butt each other to fight for scarce food
Video experiments show that monarch caterpillars turn aggressive when there’s not enough milkweed to go around.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGuttural toads shrank by a third after just 100 years on two islands
Introduced in the 1920s, toads on two islands in the Indian Ocean have shrunken limbs and bodies that may be evidence that "island dwarfism" can evolve quickly.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsHundreds of new genomes help fill the bird ‘tree of life’
More than 10,000 bird species live on Earth. Now, researchers are one step closer to understanding the evolution of all of this feathered diversity.
By Jake Buehler -
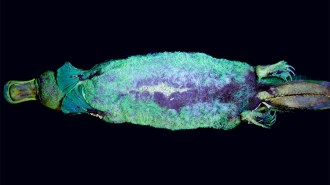 Animals
AnimalsA blue-green glow adds to platypuses’ long list of bizarre features
The discovery of platypuses’ fluorescent fur has researchers wondering if the trait is more widespread among mammals than anyone has realized.
-
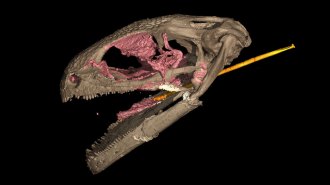 Life
LifeAn ancient amphibian is the oldest known animal with a slingshot tongue
A tiny amphibian that lived 99 million years ago waited for invertebrate prey before snatching them with a swift, shooting tongue.