Chemistry
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryGut microbes may flush ‘forever chemicals’ from the body
Experiments in mice show that some gut bacteria can absorb toxic PFAS chemicals, allowing animals to expel them through feces.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryModified bacteria convert plastic waste into pain reliever
With genetic tweaks, E. coli turned 92 percent of broken-down plastic into acetaminophen, charting a path to upcycle plastic waste sustainably.
By Skyler Ware -
 Earth
EarthClimate change is coming for your cheese
Adapting to climate change by replacing grass in cows' feed with corn affected the nutritional value and quality of cheese, French researchers found.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryLotions and perfumes affect the air near our skin
The personal care products suppress reactions between skin oils and ozone. It's not clear how, or if, this chemistry change might impact human health.
By Skyler Ware -
 Chemistry
ChemistryA chemical in plastics is tied to heart disease deaths
In 2018, over 350,000 excess heart disease deaths were linked to phthalates. More research is needed to fully understand the chemicals' effects.
By Skyler Ware -
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists home in on alternatives to ‘forever chemicals’
Bulky molecules mimic some properties of PFAS without their long-lasting chemical bonds and could replace PFAS in some water-repelling applications.
By Skyler Ware -
 Space
SpaceFermenting miso in orbit reveals how space can affect a food’s taste
A miso test on the International Space Station shows fermenting food is not only possible in space, it adds nuttier notes to the Japanese condiment.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryA new iron compound hints ‘primordial’ helium hides in Earth’s core
Earth’s core could contain helium from the early solar system. The noble gas tucks into gaps in iron crystals under high pressure and temperature.
By Skyler Ware -
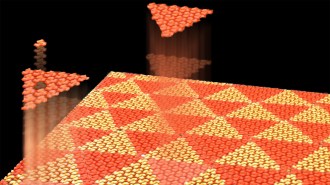 Math
MathThe einstein tile rocked mathematics. Meet its molecular cousin
Chemists identify a single molecule that naturally tiles in nonrepeating patterns, which could help build materials with novel electronic properties.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceAncient Mars wasn’t just wet. It was cold and wet
Mars may once have held enough water to fill oceans and form coastlines. The planet’s red dust contains water and likely formed in cold conditions.
By Skyler Ware -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineToxic dangers lurk in LA, even in homes that didn’t burn
Urban wildfires like LA’s make harmful chemicals from burning plastics and electronics that can make indoor air dangerous for months.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryA new microbead proves effective as a plastic-free skin scrubber
The nonplastic polymer cleaned up eyeliner and permanent marker and broke down into molecules related to sugar and amino acids.
By Skyler Ware