Chemistry
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
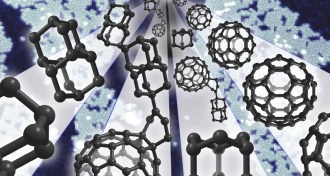 Materials Science
Materials ScienceBuckyballs, diamonds inspire new synthetic molecule
Hitching a hollow ball of carbon to a diamond-shaped lattice yields a useful piece of electrical circuitry.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryLiquid salts break through armored bacteria on skin
Compounds called ionic liquids can penetrate bacterial biofilms on skin to deliver antibiotics to potentially life-threatening infections.
By Sam Lemonick -
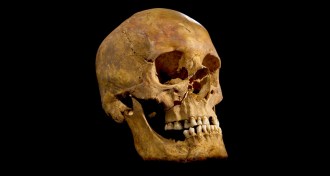 Anthropology
AnthropologyRichard III ate like a king before biting the dust
King Richard III’s brief reign included a sudden shift to eating fancy food and drink.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
ChemistryMolecular cage traps rare gases
Organic compound could cull valuable xenon from the air and detect cancer-causing radon in homes.
By Beth Mole -
 Chemistry
ChemistryBoron atoms take on buckyball shape
The first boron buckyball-like molecule could be used for storing hydrogen, scientists suggest.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMysterious neurotoxin may help flatworms kill prey
Tetrodotoxin, the deadly chemical in pufferfish, could help flatworms transform their earthworm prey into puddles of goo.
By Beth Mole -
 Chemistry
ChemistrySafe salt could yield cheaper, more efficient solar cells
Magnesium chloride could be the key ingredient for concocting efficient solar cells with cadmium telluride.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘Prisoners, Lovers, and Spies’ reveals the secrets of invisible ink
Kristie Macrakis takes readers on a tour of invisible ink’s history and the need to hide information, from the earliest empires to the Internet age.
By Bryan Bello -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMoon’s origins revealed in rocks’ chemistry
A new chemical measurement of rocks from Earth and from the moon supports the giant impact hypothesis, which explains how the moon formed billions of years ago.
By Meghan Rosen -
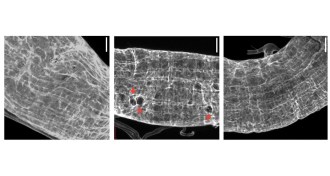 Genetics
GeneticsBromine found to be essential to animal life
Fruit flies deprived of the element bromine can’t make normal connective tissue that supports cells and either don’t hatch or die as larvae.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryDecay of Leonardo da Vinci drawing reflected in light
Light that bounces off a Leonardo da Vinci drawing, widely considered a self-portrait, has revealed extensive chemical damage that causes yellowing.
By Beth Mole -
 Chemistry
ChemistryBacteria take plants to biofuel in one step
Engineered bacterium singlehandedly dismantles tough switchgrass molecules, making sugars that it ferments to make ethanol.
By Beth Mole