Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Climate
ClimateCold War–era spy satellite images show Himalayan glaciers are melting fast
Declassified spy satellite photographs reveal that glacier melt in the Himalayas has sped up dramatically in the last two decades.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHow seafood shells could help solve the plastic waste problem
Chitin and chitosan from crustacean shells could put a dent in the world’s plastic waste problem.
By Carmen Drahl -
 Earth
EarthIs a long-dormant Russian volcano waking up? It’s complicated
Scientists debate how to interpret seismic activity near Bolshaya Udina on the remote Kamchatka Peninsula.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsMany of the world’s rivers are flush with dangerous levels of antibiotics
Antibiotic pollution can fuel drug resistance in microbes. A global survey of rivers finds unsafe levels of antibiotics in 16 percent of sites.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentSome Canadian lakes still store DDT in their mud
Yesterday’s DDT pollution crisis is still today’s problem in some of Canada’s lakes.
-
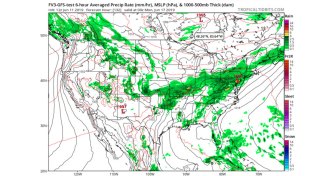 Climate
ClimateThe National Weather Service has launched its new U.S. forecasting model
The United States has finally unveiled its new, highly touted weather prediction model, but some scientists worry that it’s not ready for prime time.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureThe U.S. is still using many pesticides that are banned in other countries
In 2016, the United States used millions of kilograms of pesticides that are banned or being phased out in the European Union, Brazil and China.
-
 Oceans
OceansTiny plastic debris is accumulating far beneath the ocean surface
Floating trash patches scratch only the surface of the ocean microplastic pollution problem.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLimiting global warming to 1.5 degrees C could prevent thousands of deaths in the U.S.
A study projecting heat-related mortality in 15 U.S. cities illustrates urban risk from global warming.
-
 Earth
EarthSoil eroded by glaciers may have kick-started plate tectonics
How plate tectonics got going is a mystery. Now scientists say they’ve found a key part of the story: massive piles of sediment dumped in the ocean.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentChemicals in biodegradable food containers can leach into compost
PFAS compounds from compostable food containers could end being absorbed by plants and later eaten by people, though the health effects are unclear.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThe Smithsonian’s ‘Deep Time’ exhibit gives dinosaurs new life
The Smithsonian’s renovated fossil hall puts ancient dinosaurs and other creatures in context.