Genetics
-
 Genetics
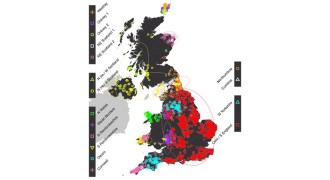
GeneticsHistory of the United Kingdom revealed in its genes
A genetics study finds subtle differences that reveal secrets about the history and ancestry of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
-
 Humans
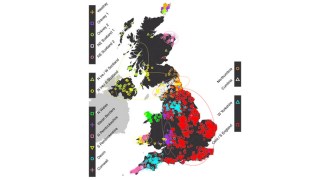
HumansHistory of the United Kingdom revealed in its genes
A genetics study finds subtle differences that reveal secrets about the history and ancestry of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe upside of a demolished chromosome
A woman’s rare genetic disease was cured when a chromosome carrying the mutant gene shattered.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsProtein comparisons proposed in 1960s for tracking evolution
In 1965, two scientists spotted molecular signatures of primate divergence. The tool became widespread for studying evolution – and one researcher’s career ended in crime.
-
 Anthropology
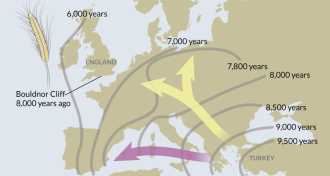
AnthropologyWheat reached England before farming
European hunter-gatherers may have traded for agricultural products 8,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeGene study digs into partnership between fungi and plants
Fungal genes for symbiotic relationship with plants evolved a few times, and relatively recently, a study suggests.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyGene variant may foretell success in program for at-risk kids
Disruptive children with DNA twist show biggest turnaround with 10-year intervention.
By Bruce Bower -
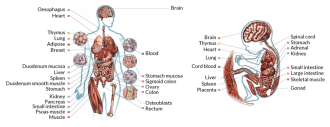 Genetics
GeneticsCatalog of DNA modifications produces surprises
A map of chemical modifications of DNA and its associated proteins shows how the genome changes during development and disease.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsFor penguins, it’s a matter of no taste
Penguins lack taste genes for bitter, sweet and umami.
-
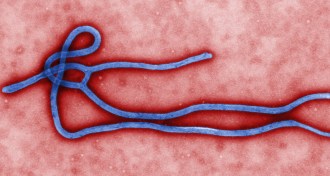 Genetics
GeneticsEbola virus evolution tracked by genetic data
Analysis of Ebola genomes shows how the virus has evolved and some of the mutations that may thwart treatments.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiger swallowtail genome gives clues to insect’s stinky defense
Clues within the genetic code of the Eastern tiger swallowtail butterfly (Papilio glaucus) explain how it developed a smelly defense against predators.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient East Asians mixed and mingled multiple times with Neandertals
East Asians’ ancestors interbred with Neandertals more than once, explaining why modern East Asians carry more Neandertal DNA than Europeans do, two studies suggest.