Genetics
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimple blood test detects heart transplant rejection
Heart transplant recipients whose bodies are starting to reject the new organ might carry genetic warning signs.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsGene variant tied to diabetes in Greenlanders
Greenlanders who carry two copies of a newly discovered gene variant have upwards of 10 times the chance of developing type 2 diabetes.
-
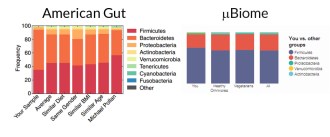 Life
LifeHere’s the poop on getting your gut microbiome analyzed
One Science News writer donated her used toilet paper for science and learned that microbiome research is as uncharted as the Wild West.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow you bet is affected by your genes
When betting, people's decisions are influenced by variations in a set of genes that regulate the brain chemical dopamine.
-

-
 Genetics
GeneticsChimp and human lineages may have split twice as long ago as thought
New estimates of chimpanzee mutation rates suggest humans and chimps last shared a common ancestor 13 million years ago.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWool pulled from sheep’s genetic code
Sheep's genetic sequence, comprised of 2.6 billion base pairs, offers clues to how the animals maintain extra woolly coats and when they evolved from other livestock.
-
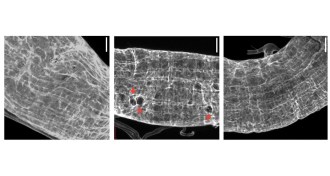 Genetics
GeneticsBromine found to be essential to animal life
Fruit flies deprived of the element bromine can’t make normal connective tissue that supports cells and either don’t hatch or die as larvae.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsBlind mole-rats are loaded with anticancer genes
Genes of the long-lived blind mole-rat help explain how the animal evades cancer and why it lost vision.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryBacteria take plants to biofuel in one step
Engineered bacterium singlehandedly dismantles tough switchgrass molecules, making sugars that it ferments to make ethanol.
By Beth Mole -
 Microbes
MicrobesIrish potato famine microbe traced to Mexico
The pathogen that triggered the Irish potato famine in the 1840s originated in central Mexico, not the Andes, as some studies had suggested.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow a genetic quirk makes hair naturally blond
Natural blonds don’t need hair dye. They have a variation on a genetic enhancer that dampens pigment production in their hair follicles, scientists say.