Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
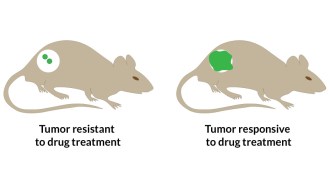
Health & MedicineCancer killers send signal of success
Newly designed nanoparticles deliver anticancer drugs and updates on tumor death.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsZika may have flown to Brazil in 2013
The brand of Zika currently floating around the Americas traces its origins to Asia and may have arrived in Brazil by air as early as 2013.
-
 Life
LifeRacing for answers on Zika
In the latest issue of Science News, Editor in Chief Eva Emerson talks Zika virus, microbes, nutrition and mental health.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMicrobes can play games with the mind
Our bodies are having a conversation with our microbiome that may be affecting our mental health — for better or worse.
-
 Neuroscience
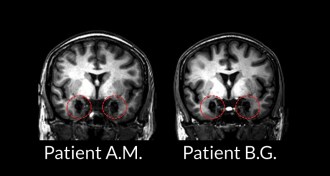
NeuroscienceBrain holds more than one road to fear
A study on rare patients suggests that fear can take many paths through the brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
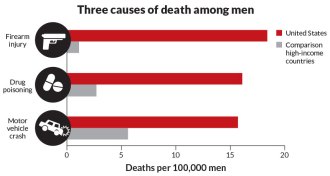
Health & MedicineThree big reasons why U.S. men have a shorter life expectancy
U.S. men’s lives are two years shorter than men in other rich countries for three reasons: guns, drugs and cars.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSpecial Report: Here’s what we know about Zika
Tracing Zika’s path and its potential links to microcephaly in babies and Guillain-Barré syndrome has scientists planning a new war on mosquitoes.
-
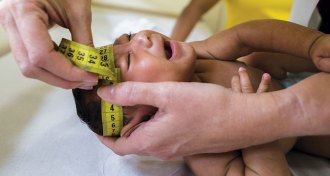 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow Zika became the prime suspect in microcephaly mystery
New evidence in human cells strengthens the case against Zika in Brazil's microcephaly surge, but more definitive proof could come this summer from Colombia.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEfforts to control mosquitoes take on new urgency
The major mosquito that is spreading Zika virus has quirks that make it one of the toughest to fight.
By Susan Milius -
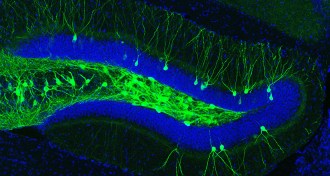 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLost memories retrieved for mice with signs of Alzheimer’s
Using light, scientists coaxed a forgotten memory from the brains of mice with Alzheimer’s-like symptoms.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsFDA predicts no significant environmental impact from GM mosquitoes
The FDA has taken a step in the process of deciding whether to allow the first test release in the United States of genetically modified mosquitoes to fight diseases such as Zika.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s how dust mites give dermatitis sufferers the itch
Dust mites can make people with eczema truly miserable. Now, scientists have figured out why they make some people scratch, and resolved a dermatological debate.