Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
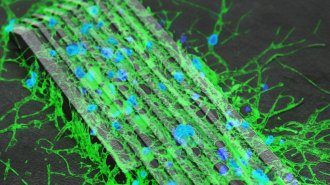
NeuroscienceTiny, magnetically controlled robots coax nerve cells to grow connections
Research using microrobots and nerve cells from rats could point to new treatments for people with nerve injuries.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA Brazilian city devastated by COVID-19 may have reached herd immunity
Up to half of Manaus was infected at the epidemic’s peak, which slowed further spread of the virus but also led to many deaths, scientists say.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEarly immune responses may be why younger people get less sick from COVID-19
Age-related differences in coronavirus immune defenses hint that a boost in early immune responses from drugs or a vaccine could help protect people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibodies made in the lab show some promise for treating COVID-19
Preliminary results from two companies hint that the proteins can help COVID-19 patients from needing hospitalization or ventilation.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat will happen when COVID-19 and the flu collide this fall?
As the Northern Hemisphere braces for a coronavirus-flu double hit, it’s unclear if it’ll be a deadly combo or one virus will squeeze out the other.
-
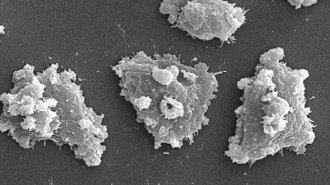 Microbes
Microbes50 years ago, scientists were on the trail of a brain-eating amoeba
In 1970, scientists were studying a brain-eating amoeba that had been implicated in a newfound disease. Today, infections by the parasite are still poorly understood.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologySeven footprints may be the oldest evidence of humans on the Arabian Peninsula
In what’s now desert, people and other animals stopped to drink at a lake more than 100,000 years ago, a new study suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
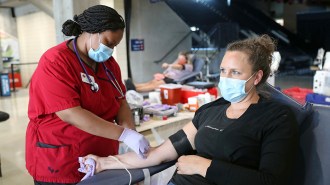 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlood donations show that the United States is still nowhere near herd immunity
Testing donated blood for antibodies to the coronavirus highlights that the vast majority of the United States remains susceptible to infection.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘The Origins of You’ explores how kids develop into their adult selves
A new book describes the interplay of nature and nurture as children, at least in Western societies, grow up.
By Bruce Bower -
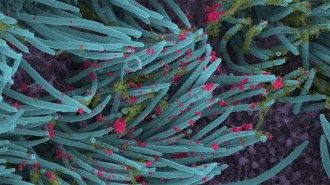 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLung cell images show how intense a coronavirus infection can be
Microscopic views reveal virus particles coating the hairlike cilia of an airway cell from the lungs.
-
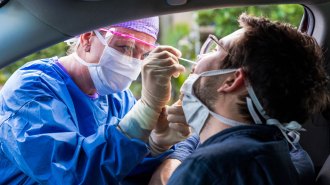 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTreatments that target the coronavirus in the nose might help prevent COVID-19
Scientists are developing and testing ways to prevent the virus from settling in prime nasal real estate.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCollege athletes show signs of possible heart injury after COVID-19
Four of 26 college athletes, who had mild or asymptomatic COVID-19, may have had myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle.