Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow two immune system chemicals may trigger COVID-19’s deadly cytokine storms
A study in mice hints at drugs that could be helpful in treating severe coronavirus infections.
-
 Anthropology
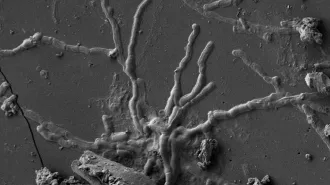
AnthropologyThese human nerve cell tendrils turned to glass nearly 2,000 years ago
Part of a young man’s brain was preserved in A.D. 79 by hot ash from Mount Vesuvius’ eruption.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyThe first Denisovan DNA outside Siberia unveils a long stint on the roof of the world
Genetic evidence puts Denisovans, humankind’s now-extinct cousins, on the Tibetan Plateau from 100,000 to at least 60,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMummified llamas yield new insights into Inca ritual sacrifices
Bound and decorated llamas, found at an Inca site in southern Peru, may have been buried alive as part of events in annexed territories.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansThe longest trail of fossilized human footprints hints at a risky Ice Age trek
Researchers have discovered the world's longest trail of fossilized human footprints at White Sands National Park, New Mexico.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy bat scientists are socially distancing from their subjects
Scientists are calling for a “hands-off” approach to research to decrease the chances of spreading the coronavirus to bats in North America.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe arthritis drug tocilizumab doesn’t appear to help fight COVID-19
The best available evidence so far hasn’t found that the anti-inflammatory drug benefited patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHomo erectus, not humans, may have invented the barbed bone point
Carved artifacts excavated from Tanzania’s Olduvai Gorge suggest now-extinct hominids made barbed bone points long before humans did, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow environmental changes may have helped make ancient humans more adaptable
An East African sediment core unveils ecological changes underlying a key Stone Age transition.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansWe still don’t know what COVID-19 immunity means or how long it lasts
Without knowing how long immunity lasts, it may be impossible to reach herd immunity without a vaccine or an extremely high death toll.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHeating deltamethrin may help it kill pesticide-resistant mosquitoes
A simple chemical trick creates a much faster-acting form of a common insecticide, which could help fight malaria and other mosquito-borne illnesses.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRemdesivir doesn’t reduce COVID-19 deaths, a large WHO trial finds
An international study of more than 11,000 people finds that remdesivir doesn’t prevent deaths from COVID-19, but the drug may still be useful.