Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene editing creates virus-free piglets
Pigs engineered to lack infectious viruses may one day produce transplant organs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore U.S. adults are drinking, and more heavily
Heavy drinking and alcohol use disorders have risen in the United States, at a cost to society’s health.
-
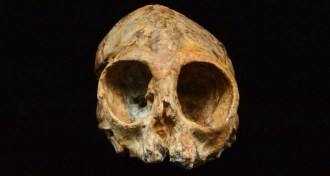 Anthropology
AnthropologyInfant ape’s tiny skull could have a big impact on ape evolution
Fossil comes from a lineage that had ties to the ancestor of modern apes and humans, researchers argue.
By Bruce Bower -
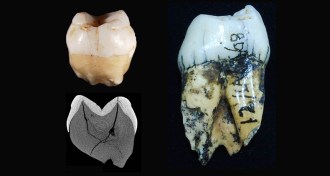 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient people arrived in Sumatra’s rainforests more than 60,000 years ago
Humans reached Indonesia not long after leaving Africa.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
PsychologyA look at Rwanda’s genocide helps explain why ordinary people kill their neighbors
New research on the 1994 Rwanda genocide overturns assumptions about why people participate in genocide. A sense of duty, not blind obedience, drives many perpetrators.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyTo combat cholera in Yemen, one scientist goes back to basics
As the cholera epidemic rages on in war-torn Yemen, basic hygiene is the first line of defense.
-
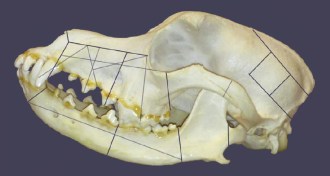 Anthropology
AnthropologySacrificed dog remains feed tales of Bronze Age ‘wolf-men’ warriors
Canine remnants of a possible Bronze Age ceremony inspire debate.
By Bruce Bower -
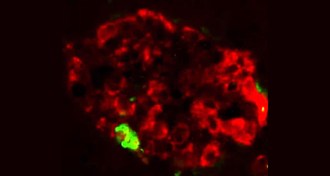 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSpread of misfolded proteins could trigger type 2 diabetes
Experiments in mice raise the question of whether type 2 diabetes might be transmissible.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen kids imitate others, they’re just being human
In imitation tests, kids readily performed nonsensical actions, but bonobos didn’t. The results hint that excessive imitation may be a uniquely human trait.
-
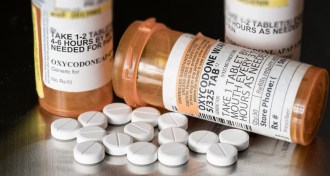 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOne in three U.S. adults takes opioids, and many misuse them
More than a third of U.S. adults used prescription opioids in 2015, and nearly 13 percent of that group misused the painkillers in some way.
By Kate Travis -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOne in three U.S. adults takes opioids, and many misuse them
More than a third of U.S. adults used prescription opioids in 2015, and nearly 13 percent of that group misused the painkillers in some way.
By Kate Travis -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice with a mutation linked to autism affect their littermates’ behavior
Genetically normal littermates of mutated mice behave strangely, suggesting that the social environment plays a big role in behavior.