Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Tech
TechPill measures gut gas
A gas-sensing ingestible capsule tested in pigs could someday help doctors assess people’s gastrointestinal health.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMouse study offers clues to brain’s response to concussions
The brain needs time to recover between head hits, a study in mice suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
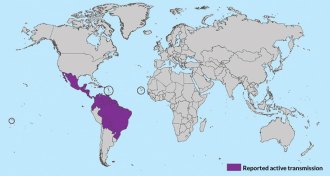
Health & MedicineWHO declares international emergency for cases linked to Zika virus
The recent spate of birth defects and neurological disorders linked to Zika virus infection constitutes an international public health emergency, the World Health Organization declared February 1.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
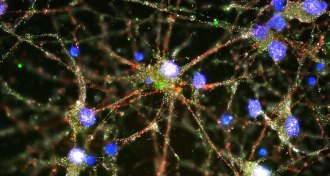
NeuroscienceImmune system gene leads to schizophrenia clue
Excessive snipping of nerve cell connections may contribute to schizophrenia.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyBabylonians used geometry to track Jupiter’s movements
Babylonians took a geometric leap to track Jupiter’s movements long before European astronomers did.
By Bruce Bower -
 Tech
TechTracking health is no sweat with new device
New all-in-one electronic device can detect and analyze your temperature and four chemicals in your sweat.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMonkeys with human gene show signs of autism
Genetically altered monkeys may help scientists understand autism.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyThere’s a sour side to serotonin
Serotonin has a sour side. The chemical messenger helps mice to taste sour, a new study shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRapid spread of Zika virus in the Americas raises alarm
After blazing through Brazil, a mosquito-borne virus called Zika, which may cause birth defects, is now poised to jump to the United States.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNoisy toys mute conversations
Electronic toys put a damper on the conversations between parents and babies.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAttack 10,000 years ago is earliest known act of warfare
Human skeletons unearthed in East Africa show signs of a roughly 10,000-year-old lethal raid.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansNo fairy tale: Origins of some famous stories go back thousands of years
Pairing folktales with ancient languages shows that at least a few folktales originated thousands of years ago.