Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsFDA predicts no significant environmental impact from GM mosquitoes
The FDA has taken a step in the process of deciding whether to allow the first test release in the United States of genetically modified mosquitoes to fight diseases such as Zika.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s how dust mites give dermatitis sufferers the itch
Dust mites can make people with eczema truly miserable. Now, scientists have figured out why they make some people scratch, and resolved a dermatological debate.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsFinding wonders in fat
In the latest issue of Science News, Editor in Chief Eva Emerson talks fat cells, thermodynamics, and lead poisoning.
By Eva Emerson -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceReaders respond to stress, tattoos, and the universe
Stress, tattoos, cosmic origins and more reader feedback.
-
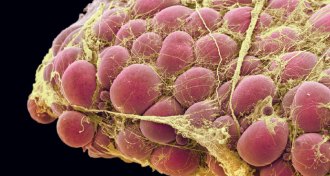 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCells from fat mend bone, cartilage, muscle and even the heart
Stem cells and other components of fat can be coerced to grow into bone, cartilage, muscle or to repair the heart.
By Susan Gaidos -
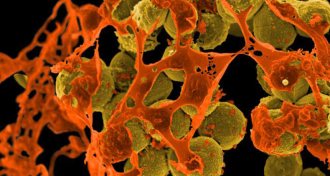 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMolecules found to counter antibiotic resistance
Molecules made in a lab can foil antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew techniques regrow lens, cornea tissue
Preliminary stem cell discoveries may restore lenses and corneas.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyH. erectus cut, chewed way through evolution
A diet that included raw, sliced meat changed the face of early Homo evolution, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Cancer moonshot’ launch prep under way
Details are trickling out for the president’s proposed “cancer moonshot,” but plan for launch is still months off.
By Laura Beil -
 Climate
ClimateHurricane frequency dropped during 17th century ‘Little Ice Age’
Atlantic hurricane activity fell around 75 percent when the sun dimmed from 1645 to 1715, a new analysis of shipwrecks and tree rings suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEat your stinkbugs
Prepared as a snack by some groups in southern Africa, the stinkbug Encosternum delegorguei is a good source of protein and antioxidants.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMind’s healing powers put to the test in new book
Cure: A Journey Into the Science of Mind Over Body investigates the brain’s role in keeping people healthy.