Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBroken bones heal with young blood, how remains a mystery
Blood from young mice rejuvenates bones of elderly mice, but how it works remains a mystery.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsPandas’ gut bacteria resemble carnivores’
Unlike other vegetarians, the bamboo eaters lack plant-digesting microbes.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Environment
EnvironmentE-cigarette flavorings may harm lungs
Certain e-cigarette flavors, such as banana pudding, may damage lung tissue
By Beth Mole -
 Life
LifeTypical American diet can damage immune system
The typical American diet sends our good and bad gut microbes out of balance and can lead to inflammation and a host of problems.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA firm grip may predict risk of death better than blood pressure
The strength of people’s grip could predict how likely they are to die if they develop cardiovascular or other diseases.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyQuantity counts for baboons
Counting-like logic helps baboons track and compare accumulating sets of peanuts.
By Bruce Bower -
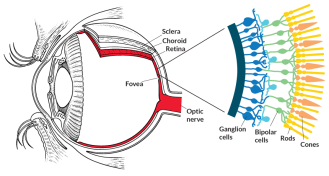 Genetics
GeneticsHow to rewire the eye
The cutting-edge technology called optogenetics may offer a workaround to partially restore vision even after the retina’s light-sensing rods and cones die.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEarly research asked whether cats dream
Early research asked whether cats dream; researchers still don’t know definitively.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsQuicker sepsis diagnosis may be a step closer
Identifying genes linked with sepsis may make it possible to develop a blood test to diagnose the infection days sooner than current methods.
-
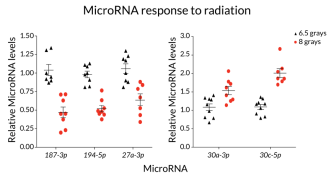 Genetics
GeneticsMicroRNAs track radiation doses
MicroRNAs in the blood may indicate radiation damage, a study of mice finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBirth-weight boost tied to cleaner air during Beijing Olympics
Babies whose eighth month of gestation fell during the 2008 Beijing Olympics were born slightly heavier than babies born a year earlier or later, a stark indication of the effects of pollution on development.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineToo much light slows brown fat, suggesting link with obesity
Brown fat is supposed to be the friendly kind, but making the days longer with artificial light may turn it into an enemy in the battle against obesity.