Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyPots from hunter-gatherer site in China tell tale of lifestyle shift
Chinese foragers settled down and made pottery shortly before farming’s ascent.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyRitual cannibalism occurred in England 14,700 years ago
Human bones show signs of ritual cannibalism in England 14,700 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
PsychologyTo reduce stress and anxiety, make yourself invisible
We may not be able to make people invisible, but researchers have discerned its effect on the human mind in a new study.
-

-
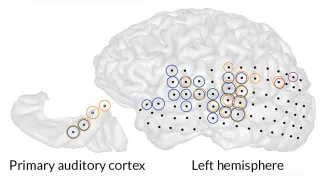 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTinnitus causes widespread trouble
People don’t just hear the phantom ringing of tinnitus in the part of the brain that processes sounds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCatching Zs may snag memories, too
Flies genetically destined to be forgetful could boost their memory with sleep.
-
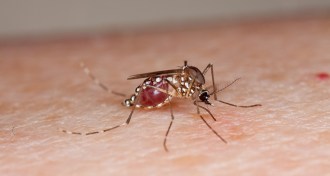 Genetics
GeneticsMosquito bites might be foretold in genes
Attractiveness to mosquitoes could be inherited, twin study suggests.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsParticle hunting in space, life in the urban jungle and more reader feedback
Readers discuss wheat's journey to England, share stories about urban wildlife and more.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScience may get sidelined in artificial turf debate
Despite news reports about the potential harms of artificial turf, studies find synthetic fields have few health risks, although lead levels may be elevated in older fields.
By Beth Mole -
 Psychology
PsychologyBig ears don’t necessarily come with baggage
In a small study, adults judged children and teens with big ears as intelligent and likable.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe greatest natural disaster that almost was
The public’s response to the widest tornado ever recorded suggests earlier warnings need to be done right.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBeing watched can boost productivity
In the company of another, a monkey steps up production on a simple job.