Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
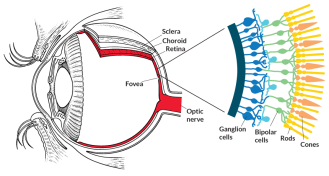
GeneticsHow to rewire the eye
The cutting-edge technology called optogenetics may offer a workaround to partially restore vision even after the retina’s light-sensing rods and cones die.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEarly research asked whether cats dream
Early research asked whether cats dream; researchers still don’t know definitively.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsQuicker sepsis diagnosis may be a step closer
Identifying genes linked with sepsis may make it possible to develop a blood test to diagnose the infection days sooner than current methods.
-
 Genetics
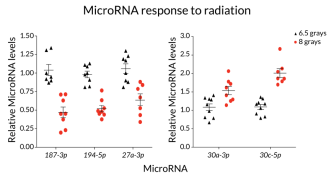
GeneticsMicroRNAs track radiation doses
MicroRNAs in the blood may indicate radiation damage, a study of mice finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBirth-weight boost tied to cleaner air during Beijing Olympics
Babies whose eighth month of gestation fell during the 2008 Beijing Olympics were born slightly heavier than babies born a year earlier or later, a stark indication of the effects of pollution on development.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineToo much light slows brown fat, suggesting link with obesity
Brown fat is supposed to be the friendly kind, but making the days longer with artificial light may turn it into an enemy in the battle against obesity.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsMolecular scissors snip at cancer’s Achilles’ heel
Finding cancer’s vulnerable spots using CRISPR technology could lead to drugs that hit the disease hard.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsHumans and Neandertals mated more recently than thought
Neandertals and humans interbred in Europe until shortly before Neandertals went extinct.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChildren’s cells live on in mothers
A baby's cells knit their way into a mother’s body.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKids who have had measles are at higher risk of fatal infections
Measles infection leaves kids vulnerable to other infectious diseases for much longer than scientists suspected.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Psychology
PsychologyOn Facebook, you control the slant of the news you choose
Facebook users shield themselves from opposing political ideas more than the site does.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyWandering planets, the smell of rain and more reader feedback
Readers consider how hard it would be to fashion Paleolithic tools, discuss what to call free-floating worlds and more.