Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineJet lag affects gut microbes
Jet-lagged bacteria in the gut impair mice’s metabolism, causing obesity and diabetes-related problems.
-
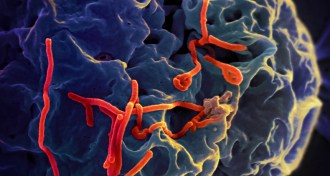 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola continues rapid spread in West Africa
Ebola continues to spread in West Africa, but some countries are poised to declare victory over the deadly virus.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient Greek shipwreck found to be world’s largest
Special diving suits enable discovery that much of a nearly 2,100-year-old Greek vessel and its cargo survive.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePneumococcal vaccine thwarts resistant infections in children
Since a new vaccine was introduced in 2010, the number of antibiotic-resistant pneumococcal infections in kids has plunged.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDrug appears safe in children with C. difficile infections
Early test suggests adult med may work in kids with diarrheal disease.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDallas health worker is first to catch Ebola in U.S.
A health worker in Dallas has Ebola. She is the first to catch the virus in the U.S.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDrug-resistant staph common in football players
Athletes in contact sports should wash their hands (and dirty gym clothes) often, researchers say.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImpotence drug boosts insulin in some with diabetes
A drug called yohimbine lets some people with diabetes secrete more insulin by stopping pancreas cells from binding adrenaline molecules.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA timeline of a baby’s first hour
A study carefully documents newborns’ instinctual behaviors in the first hour outside the womb, observations that paint a picture of what babies might need in the moments after birth.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesGut bacteria protein linked to anorexia and bulimia
Gut bacteria may play a role in eating disorders, a new study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFirst Ebola patient diagnosed in U.S. dies
Thomas Eric Duncan, who contracted the virus in Liberia and fell ill four days after traveling to Dallas, died October 8.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyIndonesian stencils rival age of Europe’s early cave art
Hand prints outlined in pigment were made in Southeast Asia at least 39,900 years ago, making the paintings about the same age as European cave art.
By Bruce Bower