Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBone marrow transplant could reverse sickle cell in adults
A relatively mild treatment involving radiation and chemo followed by a bone marrow transplant may treat sickle cell disease in adults.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologyTablet devices help kids with autism speak up
Talking iPads may help break the near-silence of some kids with autism.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKids’ me time may boost brainpower
Unstructured play may give kids more opportunity to exercise their executive function, complex cognitive function that includes resisting impulses and paying attention.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceShaking up the body may improve attention
Just two minutes of whole body vibrations improved young adults’ attention to detail.
-
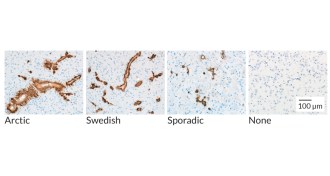 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s disease may come in distinct forms
Mouse experiments, if confirmed in people, imply that Alzheimer’s disease treatment should be personalized.
-
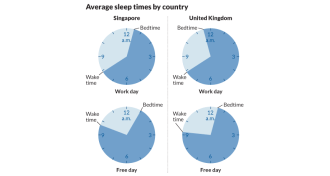 Psychology
PsychologyWesterners sleep more than people from Eastern nations
Sleep schedules vary from country to country, with social demands like work and study providing the primary incentives to stay up.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyOnline causes may attract more clicks than commitments
Online awareness campaigns can make people feel they’ve contributed to a good cause, but social scientists say the tangible benefits of such efforts may be small.
By Bruce Bower -
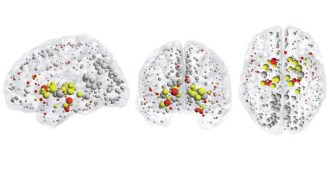 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBusy brain hubs go awry in disorders, study suggests
Schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s and other brain disorders may occur when the brain’s most active hubs are damaged.
-
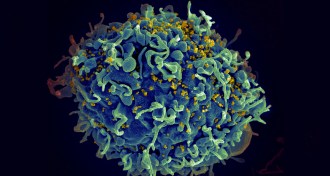 Life
LifeHIV hides in growth-promoting genes
The discovery that HIV can trigger infected cells to divide means scientists may need to rethink strategies for treating the virus that causes AIDS.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyNeanderthals reveal their diet with oldest excrement
50,000-year-old fossil poop hints at Neanderthals’ omnivorous, but meat-heavy, diet.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHidden heart rhythm problem may underlie some strokes
In two clinical studies, people who had had strokes with no trigger sometimes also had undiagnosed atrial fibrillation.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYour baby can watch movies for science
Any parent with a computer can let their kid participate in child development studies through a new website called Lookit.