Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyAttractiveness studies are hot, or not
Studies that link attractiveness to other traits are often misinterpreted, including recent studies of nose bacteria and of cycling ability.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyRoman gladiator school digitally rebuilt
Imaging techniques unveil a 1,900-year-old Roman gladiators’ training center that’s buried beneath a site in Austria.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImbalance in gut bacteria may play role in Crohn’s disease
Identifying the onset of Crohn’s disease may best be done by looking at bacteria in the cellular linings intestinal tissue.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental drug might get the salt out
Tests in people and rats show sodium levels in blood drop as drug candidate limits the body’s salt absorption.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOverheard, baby edition: Making sense of new words
Eavesdropping babies learn new words when they understand familiar ones.
-
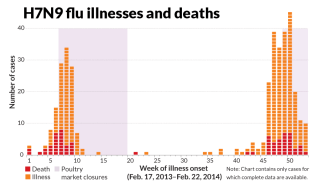 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSecond wave of bird flu ups pandemic worries
The H7N9 avian influenza virus, which first appeared in 2013, is sweeping China with a second, larger wave of illness.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMS milder when patients begin with higher vitamin D levels
Multiple sclerosis patients with low concentrations of vitamin D early in their disease have more nerve damage several years later.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologyThe addiction paradox
Addiction is often seen as a chronic disease that requires maintenance treatment even after years of sobriety. But even without help, most addicts eventually can quit for good.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCasinos may reduce poverty, obesity in Native American communities
A modest reduction in overweight youth was observed after the addition of slot machines.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeaty diets may raise risk of dying young
Reducing protein consumption can lengthen life and improve health, studies in mice and people suggest.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHPV vaccination proves its worth in Australia
A study in Australia finds the shots are already reducing cases of abnormal cervical lesions.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineShould you hush that white noise?
Some sleep machines can pump out a dangerous amount of noise, but that doesn’t mean they can’t be used safely.