Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologySmall ‘cousins’ of T. rex may actually have been growing teenagers
Fossil analyses suggest that Nanotyrannus wasn’t a diminutive relative of the more famous behemoth Tyrannosaurus rex.
By Sid Perkins -
 Health & Medicine
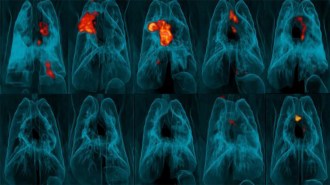
Health & MedicineInjecting a TB vaccine into the blood, not the skin, boosts its effectiveness
Giving a high dose of a tuberculosis vaccine intravenously, instead of under the skin, improved its ability to protect against the disease in monkeys.
By Tara Haelle -
 Life
LifeRussian foxes bred for tameness may not be the domestication story we thought
Foxes bred for tameness also developed floppy ears and curly tails, known as “domestication syndrome.” But what if the story isn’t what it seems?
By Jake Buehler -
 Life
LifeFluid dynamics may help drones capture a dolphin’s breath in midair
High-speed footage of dolphin spray reveals that droplets blast upward at speeds approaching 100 kilometers per hour.
-
 Life
LifeStick-toting puffins offer the first evidence of tool use in seabirds
Puffins join the ranks of tool-using birds after researchers document two birds using sticks to groom, a first for seabirds.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyScience News’ favorite fossils of 2019
Fossil discoveries reported this year included Cambrian creatures, ancient bone cancer and a peek at life’s recovery after the dinosaur die-off.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesAirplane sewage may be helping antibiotic-resistant microbes spread
Along with drug-resistant E. coli, airplane sewage contains a diverse set of genes that let bacteria evade antibiotics.
-
 Life
LifeOcean acidification could degrade sharks’ tough skin
Nine weeks of exposure to acidic seawater corroded the toothlike denticles that make up a puffadder shyshark’s skin, a small experiment found.
-
 Life
LifeKoalas aren’t primates, but they move like monkeys in trees
With double thumbs and a monkey-sized body, an iconic marsupial climbs like a primate.
By Susan Milius -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDNA from 5,700-year-old ‘gum’ shows what one ancient woman may have looked like
From chewed birch pitch, scientists recovered DNA from an ancient woman and her mouth microbes and hazelnut and duck DNA from a meal she’d consumed.
By Sofie Bates -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice watching film noir show the surprising complexity of vision cells
Only about 10 percent of mice’s vision cells behaved as researchers expected they would, a study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA year of big numbers startled the world into talking about nature
One million species are at risk. Three billion birds have been lost. Plus surges in Amazon burning.
By Susan Milius