Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScore! Bumblebees see how to sink ball in goal, then do it better
A first lesson in six-legged soccer tests bumblebees’ ability to learn.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeBacteria’s amyloids display surprising structure
Protein clusters made by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria have a surprising new structure.
-
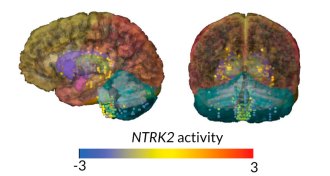 Genetics
GeneticsHuman genes often best Neandertal ones in brain, testes
Differing activity of human and Neandertal versions of genes may help explain health risks.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInstead of starving a cancer, researchers go after its defenses
There may be ways to block tumors from adapting and outrunning the body’s defenses.
By Laura Beil -
 Animals
AnimalsToo many stinkbugs spoil the wine
Stinkbugs can ruin wine if enough are accidentally processed alive with the grapes. Three or fewer stinkbugs per grape cluster don’t have a noticeable effect on red wine.
-
 Life
LifeHowler monkeys may owe their color vision to leaf hue
Better color vision gives howler monkeys an edge at finding food.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyPower may have passed via women in ancient Chaco Canyon society
DNA points to a 330-year-long reign of a maternal dynasty centered in New Mexico’s Chaco Canyon.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyLow-status chimps revealed as trendsetters
Outranked chimpanzees trigger spread of useful new behaviors among their comrades.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsCoconut crab pinches like a lion, eats like a dumpster diver
Coconut crabs use their surprisingly powerful claw for more than cracking coconuts.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsEnzymes aid rice plants’ arsenic defenses
Rice plant roots have natural defenses against arsenic.
-
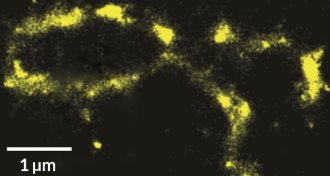 Life
LifeNew imaging technique catches DNA ‘blinking’ on
Dye-free imaging technique zooms in below 10-nanometer threshold, allowing new cellular views.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobes survived inside giant cave crystals for up to 50,000 years
Microbes trapped in crystals in Mexico's Naica mine may represent some of the most distinct life-forms found in Earth so far.