Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
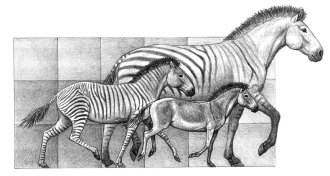
LifeHorses buck evolutionary ideas
Horse evolution doesn’t fit classic scenario of trait evolution.
-
 Life
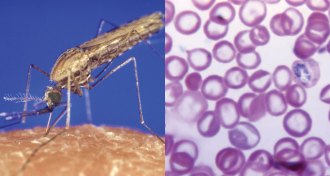
LifeMalaria molecule makes blood extra-alluring to mosquitoes
Scientists have identified a molecule that draws mosquitoes to malaria-infected blood.
-
 Animals
AnimalsYoung penguins follow false food cues
Juvenile African penguins are being trapped in barren habitats, led astray by biological cues that are no longer reliable because of human activity.
-
 Animals
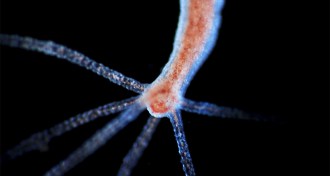
AnimalsHow hydras know where to regrow their heads
Regenerating pond animals called hydras inherit structural patterns from their original forms, researchers find.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow hydras know where to regrow their heads
Regenerating pond animals called hydras inherit structural patterns from their original forms, researchers find.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNumber of species depends how you count them
Genetic evidence alone may overestimate numbers of species, researchers warn.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsZika virus ‘spillback’ into primates raises risk of future human outbreaks
Spillback of Zika virus into monkeys may complicate eradication efforts.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMysteries of time still stump scientists
The new book "Why Time Flies" is an exploration of how the body perceives time.
-
 Climate
ClimateHot nests, not vanishing males, are bigger sea turtle threat
Climate change overheating sea turtle nestlings may be a greater danger than temperature-induced shifts in their sex ratios.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsA diet of corn turns wild hamsters into cannibals
Female European hamsters fed a diet of corn eat their young — alive. They may be suffering from something similar to the human disease pellagra.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPectoral sandpipers go the distance, and then some
Even after a long migration, male pectoral sandpipers keep flying, adding 3,000 extra kilometers on quest for mates.
-
 Earth
EarthOxygen flooded Earth’s atmosphere earlier than thought
The Great Oxidation Event that enabled the eventual evolution of complex life began 100 million years earlier than once thought, new dating of South African rock suggests.