Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
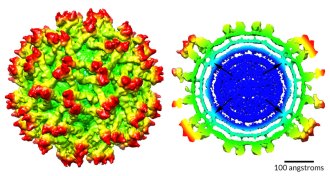
LifeMap of Zika virus reveals how it shifts as it matures
A cryo-electron microscopy map of immature Zika virus offers a never-before-seen glimpse of remodeling of the virus’s protein and RNA core.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRogue antibody linked to severe second dengue infections
Alternate antibody may indicate whether someone is susceptible to severe dengue disease.
-
 Life
LifeWhy salmonella doesn’t want you to poop out
Salmonella bacteria fight infection-driven losses in appetite to keep hosts just healthy enough for transmission.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologySnooze patterns vary across cultures, opening eyes to evolution of sleep
Sleep plays out differently across cultures, but a consistent cycle of z’s and activity appears crucial.
By Bruce Bower -
 Plants
PlantsBig genetics study blazes path for bringing back tomato flavor
Combining taste tests with genetics suggests what makes heirloom varieties tastier than mass-market tomatoes.
By Susan Milius -
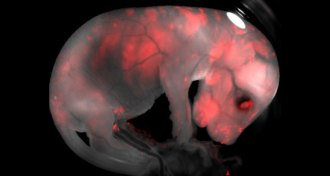 Life
LifeMouse cells grown in rats cure diabetes in mice
Mixing cells of two species produces pig and cattle embryos with some human cells.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEndings make way for new beginnings for Earth and SN
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses major changes for life on Earth and at Science News.
By Eva Emerson -
 Animals
AnimalsReaders weigh in on mathematical animals and more
Animal math, dinosaur digestion and more in reader feedback from our December 10, 2017, issue.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyWith dinosaurs out of the way, mammals had a chance to thrive
The animals that lived through the great extinction event had a range of survival strategies to get them through.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeSome lucky birds escaped dino doomsday
Dino doomsday took out early birds too, but a lucky few survived.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthDevastation detectives try to solve dinosaur disappearance
Dinosaurs and others faced massive losses 66 million years ago from an asteroid impact, volcanic eruptions or maybe a mix of the two.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBony head ornaments signal some supersized dinosaurs
Bony headwear, like bumps and horns, is tied to bigger bodies in the theropod dinosaur family tree.