Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnimals on the Move
Worldwide — on land, in the sea and in rivers, streams and lakes — wildlife is responding to rising temperatures.
-
 Life
LifeGrasshoppers’ terror outlives them
After an existence plagued by predatory spiders, the insects pass into oblivion, leaving a legacy of impoverished soil.
By Devin Powell -
 Life
LifeCalcium offers clues in mass extinction
Ocean acidification during Permian period may have caused the Great Dying.
By Devin Powell -
 Life
LifeYou have grandpa’s chromosome tips
Older fathers pass more gene-protecting DNA to their paternal grandkids.
-
 Life
LifeInvasive mite worsens honeybee viruses
Once-obscure deformed wing virus swept to prominence in honeybee colonies in Hawaiian islands as invasive pest arrived.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeMicrobes flourish under Arctic sea ice
Oceanographic expedition surprised to find photosynthetic microorganisms thriving under frozen surface.
By Devin Powell -
 Animals
AnimalsHow a mosquito survives a raindrop hit
Lightweight insects can ride a water droplet, as long as they separate from it before hitting the ground.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeAncient birds wiped out huge insects
Competition in the air trumped the advantage of extra atmospheric oxygen.
By Devin Powell -
 Life
LifeAntiaging protein helps set daily rhythms
Changing levels of sirtuin in the brain alter activity patterns in mice.
-
 Earth
EarthDefying Depth
How deep-sea creatures, and close relatives, survive tons of water weight.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Genetics
GeneticsPoppies make more than opium
A 10-gene cluster controls the flowers’ production of a valuable cough suppressant and antitumor compound.
-
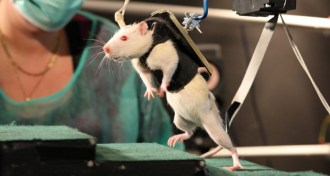 Life
LifeTreatment helps paralyzed rats walk
A combination of drugs, electrical stimulation and therapy can restore lost connections between lower limbs and brain.