Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
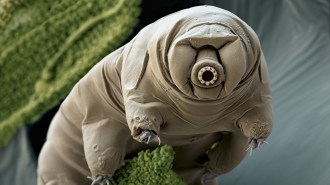
AnimalsTardigrades could teach us how to handle the rigors of space travel
Tardigrades can withstand X-rays, freezing and vacuum. Now researchers are learning how they do it, with an eye toward human space travel.
By Douglas Fox -
 Environment
EnvironmentFlower shape and size impact bees’ chances of catching gut parasites
Bumblebees have higher chances of contracting a gut parasite from short, wide flowers than from blooms with other shapes, experiments show.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe flowery scent of a Zika or dengue infection lures mosquitoes
Mice and humans infected with dengue emit acetophenone, attracting bloodsucking mosquitoes that could then transmit the viruses to new hosts.
-
 Plants
PlantsThis pitcher plant species sets its deathtraps underground
Scientists didn’t expect the carnivorous, eggplant-shaped pitchers to be sturdy enough to survive below the surface.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA newfound dinosaur had tiny arms before T. rex made them cool
A predecessor to Tyrannosaurus rex, Meraxes gigas had a giant head and puny but muscular arms, suggesting the limbs served some purpose.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEd Yong’s ‘An Immense World’ reveals how animals perceive the world
The book showcases the diverse sensory abilities of other animals and how their view of the world is different from our own.
-
 Life
LifeHere’s how sea anemones launch their venomous stingers
Starlet sea anemones use speedy projectiles to sting predators and prey. New images capture a detailed look at these weapons in action.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow scientists are shifting their search for links between diet and dementia
Studies of food’s impact on Alzheimer’s disease and dementia are hampered by complexity. Scientists hope new research approaches prove more fruitful.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFeathers may have helped dinosaurs survive the Triassic mass extinction
New data show that dinosaurs were able to weather freezing conditions about 202 million years ago, probably thanks to warm feathery coats.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyMegatooth sharks may have been higher on the food chain than any ocean animal ever
Some megalodons and their ancestors were the ultimate apex predators, outeating all known marine animals, researchers report.
By Asa Stahl -
 Animals
Animals50 years ago, eels’ navigation skills electrified scientists
Excerpt from the June 24, 1972 issue of Science News
-
 Environment
EnvironmentEarth’s oldest known wildfires raged 430 million years ago
430-million-year-old fossilized charcoal suggests atmospheric oxygen levels of at least 16 percent, the amount needed for fire to take hold and spread.
By Sid Perkins