All Stories
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyCancerous clams and other sci-fi fodder
Fans of science fiction will find a few items in this issue sure to trip the imagination.
By Eva Emerson -
 Astronomy
AstronomyWandering planets, the smell of rain and more reader feedback
Readers consider how hard it would be to fashion Paleolithic tools, discuss what to call free-floating worlds and more.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceHow did Earth get its water?
Earth is a wet planet that formed in a dry part of the solar system. How our planet’s water arrived may be a story of big, bullying planets and ice-filled asteroids.
-
 Physics
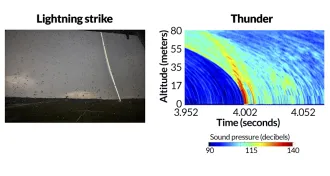
PhysicsScientists take first picture of thunder
Scientists precisely capture thunder sound waves radiating from artificially triggered lightning.
-
 Neuroscience
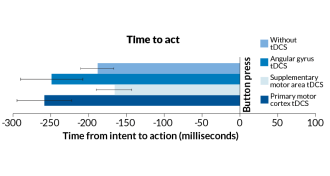
NeuroscienceStimulating nerve cells stretches time between thinking, doing
A head zap can stretch the time between intention and action.
-
 Neuroscience
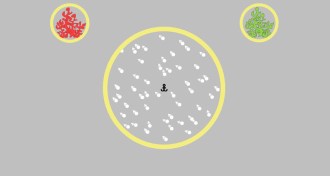
NeuroscienceChildren with autism excel at motion detection test
Children with autism outperform children without the disorder on a test that requires averaging the movements of lots of dots.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryDesigner drugs hit dangerous lows to bring new highs
A surge in designer drugs, which emulate the highs of classic illicit substances with unpredictable effects, is keeping law enforcement busy.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyOldest known avian relative of today’s birds found in China
Fossil find suggests modern birds’ oldest avian relative lived about 6 million years before previous record holder.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Physics
PhysicsNobel laureate foresees mind-expanding future of physics
A Nobel laureate forecasts deeper understanding of physics and new powers for the human mind in the century to come.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceExplore an asteroid with ‘Vesta Trek’
Vesta Trek lets users explore the asteroid Vesta with data from the Dawn spacecraft.
-
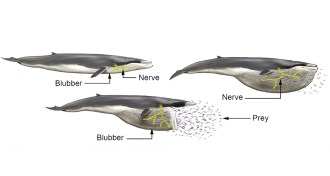 Animals
AnimalsStretchy nerves help some big whales open wide
Blue whales and their closest relatives have stretchy nerves near their mouths so they can open wide and swallow a lot of prey.
-
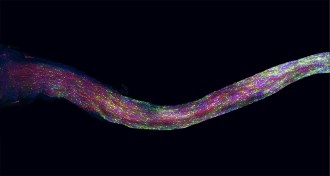 Genetics
Genetics‘Brainbow’ illuminates cellular connections
A mouse’s optic nerve fluoresces in a rainbow of colors. The image offers a detailed look at nerve-protector cells called oligodendrocytes.