All Stories
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietySometimes it’s best to feed the trolls
There are people behind malicious comments on the Internet, and sometimes engaging with them can change their behavior, data suggest.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyTo reduce stress and anxiety, make yourself invisible
We may not be able to make people invisible, but researchers have discerned its effect on the human mind in a new study.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyLit-up gas clouds hint at galaxies’ violent pasts
Voorwerpjes, tendrils of gas that orbit galaxies, continue to glow tens of thousands of years after being blasted with ultraviolet radiation.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAstronomers celebrating Hubble’s past focus on its future
Astronomers celebrate the 25th anniversary of the Hubble Space Telescope by reflecting on its diversity and looking ahead to the future.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyA peer-reviewed study finds value in peer-reviewed research
The best scoring peer-reviewed grants are associated with more papers and patents, a new study finds. But whether peer review is the best system is another question entirely.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene in human embryos altered by Chinese researchers
Chinese researchers have genetically altered human embryos.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyCosmic threesomes make some galaxies run away
Extremely rare, free-floating galaxies called compact ellipticals may have been ejected from their home clusters after a massive intergalactic meet-up.
-
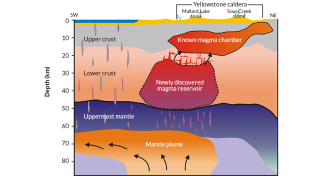 Earth
EarthMassive magma pool found deep below Yellowstone
Earthquake waves reveal massive magma reservoir deep inside the Yellowstone supervolcano.
-
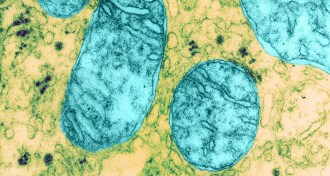 Genetics
GeneticsGenetic editing can delete deleterious mitochondria
A new technique slates mutant mitochondria for destruction.
-

-
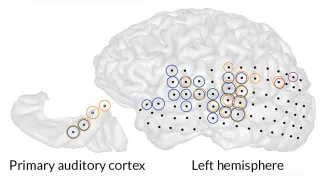 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTinnitus causes widespread trouble
People don’t just hear the phantom ringing of tinnitus in the part of the brain that processes sounds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCatching Zs may snag memories, too
Flies genetically destined to be forgetful could boost their memory with sleep.