All Stories
-
 Earth
EarthStronger quakes could strike other segments of Nepal fault
The magnitude 7.8 earthquake that struck Nepal’s capital city could be overshadowed by larger future earthquakes along the Himalayas, scientists say.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsJust 1 percent of Amazon’s trees hold half of its carbon
Roughly 1 percent of tree species in the Amazon rainforest account for half of the jungle’s carbon storage.
-
 Earth
EarthHidden water found deep beneath Antarctica desert valley
New imaging reveals liquid water network beneath Antarctica’s McMurdo Dry Valleys that could support microbial life.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFor the blind, hearing the way forward can be a tradeoff
Many blind people have enhanced hearing. A new study shows that the ability to hear your way forward might come at the cost of hearing up and down.
-
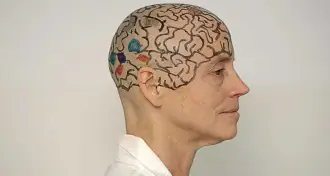 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain on display
In her online videos, Nancy Kanwisher goes where few other neuroscientists go.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWoolly mammoth DNA shows toll of low diversity
A new sequencing analysis of two woolly mammoth genomes reveals evidence of genetic decline due to isolation and inbreeding just prior to extinction.
-
 Climate
ClimateWarming’s role in extreme weather quantified
Scientists calculate how much to blame human-driven climate change for extreme high temperatures and heavy rainfall.
By Beth Mole -
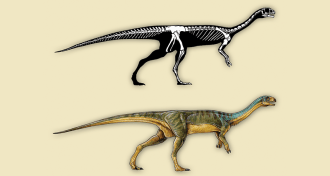 Paleontology
Paleontology‘Frankenstein’ dinosaur was a mash-up of meat eater and plant eater
Fossils of a bizarre-looking dinosaur found in Chile are challenging ideas about how dinosaurs adapted to their environments.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryA chemistry card game forges bonds
A new card game lets players brush up on chemistry by making compounds out of ions. Form some bonds and have fun in the process.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyPots from hunter-gatherer site in China tell tale of lifestyle shift
Chinese foragers settled down and made pottery shortly before farming’s ascent.
By Bruce Bower -
 Microbes
MicrobesCity- and country-dwelling microbes aren’t so different
A new study reveals the microbial communities in our nation’s dust.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyRitual cannibalism occurred in England 14,700 years ago
Human bones show signs of ritual cannibalism in England 14,700 years ago.
By Bruce Bower