News
-
 Neuroscience
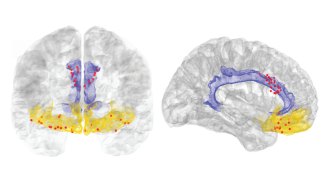
NeuroscienceBrain implants have revealed a signature for chronic pain
Brain implants in four people with chronic pain gave researchers an inside look at the debilitating condition.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSaturn’s rings may be no more than 400 million years old
An analysis of data from NASA’s defunct Cassini probe suggests Saturn's rings materialized more than 100 million years after trilobites appeared on Earth.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Life
LifeMicrowaving an insecticide restores its mosquito-killing power
Heated deltamethrin kills mosquitoes resistant to its usual form. Scientists are working to add the improved insecticide into bed nets.
-
 Humans
HumansRace car drivers tend to blink at the same places in each lap
Blinking is thought to occur randomly, but a new study tracking blinks in racing drivers shows it can be predictable — and strategic.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow over-the-counter birth control pills could improve reproductive health
The switch to over-the-counter access for a birth control pill will circumvent certain barriers and help improve reproductive autonomy.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMore than half of the world’s largest lakes are drying up
Satellite data from 1992 to 2020 reveal that 53 percent of the world’s largest freshwater bodies shrank during that period while only 24 percent grew.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Life
LifeLarge predators push coyotes and bobcats near people and to their demise
Coyotes and bobcats hide near people when wolves, cougars and other large predators are close-by, putting the smaller carnivores at a higher risk of dying at human hands.
By Freda Kreier -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAs U.S. courts weigh in on mifepristone, here’s the abortion pill’s safety record
Decades of data, including data collected during the coronavirus pandemic, support mifepristone’s safety. The drug’s fate in the United States may now be determined by judicial review.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThe oldest scaled-down drawings of actual structures go back 9,000 years
Rock engravings in Jordan and Saudi Arabia may be maps or blueprints of desert kites, massive structures once used to capture animal herds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStimulating spleens with ultrasound hints at a treatment for inflammation
Using an intense kind of ultrasound stimulation against inflammation holds promise but so far has been tested only in rodents and human blood samples.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists may have found an antidote for death cap mushrooms
A dye countered the effects of a mushroom toxin in human cells and mice. If the antidote does the same in people, it has potential to save lives.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA rare mutation helped one man stave off Alzheimer’s for decades
The brain of a Colombian man with an inherited form of Alzheimer’s may hint at ways to halt or slow the progression of the disease.
By Simon Makin