News
-
 Climate
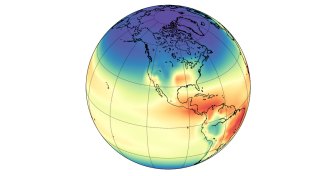
ClimatePlot twist in methane mystery blames chemistry, not emissions, for recent rise
The recent rise in atmospheric methane concentrations may have been caused by changes in atmospheric chemistry, not increased emissions from human activities, two new studies suggest.
-
 Neuroscience
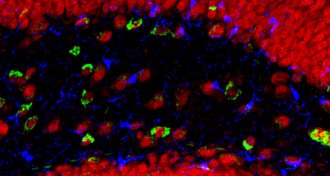
NeuroscienceBrain gains seen in elderly mice injected with human umbilical cord plasma
Plasma from human umbilical cord blood refreshes aspects of learning and memory in mice.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAutism, ADHD risk not linked to prenatal exposure to antidepressants
Taking antidepressants during pregnancy does not increase the risk of autism or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, two new large studies suggest.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyShock-absorbing spear points kept early North Americans on the hunt
Ancient Americans invented a way to make spear points last on an unfamiliar continent.
By Bruce Bower -
 Oceans
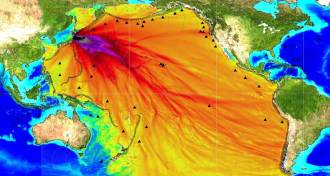
OceansMore than one ocean motion determines tsunami size
The horizontal movement of the seafloor during an earthquake can boost the size of the resulting tsunami, researchers propose.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceFood for microbes found on Enceladus
The underground ocean of Saturn’s moon Enceladus harbors an abundance of molecular hydrogen, which could be an important source of food if microbial life exists there.
-
 Chemistry
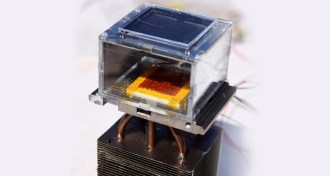
ChemistryNew tech harvests drinking water from (relatively) dry air using only sunlight
A prototype device harvests moisture from dry air and separates it into drinkable water using only sunlight.
-
 Animals
AnimalsYoung eels use magnetic ‘sixth sense’ to navigate
Migrating eels use Earth’s magnetic field.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRules restricting artificial trans fats are good for heart health
Taking artificial trans fats off the menu reduces hospitalizations for heart attack and stroke.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene knockouts in people provide drug safety, effectiveness clues
People naturally lacking certain genes give clues about drug safety and efficacy, a study in Pakistanis shows.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJupiter’s Great Red Spot has company. Meet the Great Cold Spot
A previously unidentified dark mark on Jupiter has been dubbed the “Great Cold Spot” because of its temperature and resemblance to the planet’s Great Red Spot.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPhysics trips up efforts to keep shoelaces tied
Loose laces are due to inertia and force of feet hitting the floor.