News
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsMuon surplus leaves physicists searching for answers
A glut of muons shows up in particle showers in the atmosphere.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceShape-shifting molecule aids memory in fruit flies
A prionlike protein may store long-term memories in fruit flies, a new study suggests.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCancer mutation patterns differ in smokers, nonsmokers
The DNA of smokers shows more damage than the DNA of nonsmokers who have the same kind of cancer.
-
 Climate
ClimateHuman CO2 emissions put Arctic on track to be ice-free by 2050
Sea ice is shrinking by about three square meters for each metric ton of carbon dioxide emitted, new research suggests.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyPeople settled Australia’s rugged interior surprisingly early
Ancient colonists Down Under crossed the continent not long after arriving around 50,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsGene gives mice and chipmunks their pinstripes
A recycled regulator paints on rodents’ light stripes.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEyes offer window into brain’s timekeepers
In new experiments of time perception, when pupils were large, monkeys underestimated a second.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyLearning curve not so smooth
Preschoolers tend to reach a milestone of social thinking after months of fits and starts.
By Bruce Bower -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarly birds could achieve liftoff
Early birds and other flying dinosaurs had the strong legs and wing speed needed to launch into the air directly from the ground, researchers argue.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeScientists need to redraw picture of cell’s biggest organelle
A close-up view of the cell’s endoplasmic reticulum reveals a different structure.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate change shifts how long ants hang on to coveted real estate
Simulated climate warming reveals a new pattern in turnover of ant nests.
By Susan Milius -
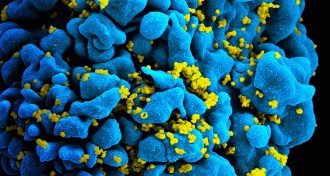 Genetics
GeneticsHIV came to NYC at least a decade before virus ID’d
DNA analysis of early viral strains tracks U.S. debut to early ’70s