News
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThese crocodile-like beasts reached the Caribbean, outlasting mainland kin
Knife-toothed reptiles called sebecids went extinct on the mainland 10 million years ago. New fossil evidence puts them on an island 4 million years ago.
By Jake Buehler -
 Tech
TechA new 3-D display lets you reach in and touch virtual objects
These hands-on displays might be used to create more immersive video games, educational tools and museum exhibits.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHere’s how we might generate electricity from rain
Water drops produce electricity when dripped through a small tube. That power might be harnessed as renewable energy in rainy places.
By Jude Coleman -
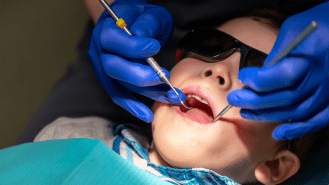 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTwo cities stopped adding fluoride to water. Science reveals what happened
As calls to end fluoride in water get louder, changes to the dental health of children in Calgary, Canada, and Juneau, Alaska, may provide a cautionary tale.
By Alex Viveros -
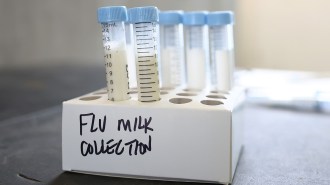 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBird flu in cows shows no signs of adapting to humans — yet
Easy replication in cattle mammary glands means H5N1 bird flu is under no evolutionary pressure to adapt to spread easily in humans.
-
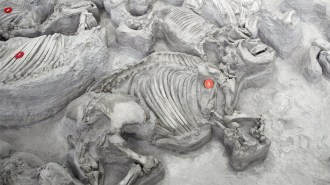 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient, water-loving rhinos gathered in big, hippolike herds
Squat rhinos lived in North America about 12 million years ago, congregating in huge, water-bound herds much like modern hippos.
By Jake Buehler -
 Earth
EarthThe United States’ oldest known rock has existed for at least 3.6 billion years
More than just a cool bit of trivia, the finding raises questions about our understanding of Earth’s history.
By Evan Howell -
 Animals
AnimalsThis caterpillar wears the body parts of insect prey
Dubbed the “bone collector,” this caterpillar found on a Hawaiian island disguises itself while stalking spider webs for trapped insects to eat.
-
 Space
SpaceSee how the Hubble Space Telescope is still revolutionizing astronomy
Hubble is still going strong 35 years after it was launched into space. Celebrate its anniversary with some out-of-this-world images.
-
 Climate
ClimateWetland bacteria could make more methane in a warming world
Warming temperatures can ramp up the activity of methane-producing bacteria in wetland soils, adding to methane emissions.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyA lion’s bite marks a fatal fight with a possible Roman-era gladiator
The first skeletal evidence of a gladiator show or execution involving an exotic animal comes from a Roman British man with bite marks from a lion.
By Bruce Bower -
 Psychology
PsychologyUncertainty is on the rise. Here’s how people can cope
Societal upheaval can trigger uncertainty, which makes people susceptible to cognitive traps. Experts suggest some simple tools can help.
By Sujata Gupta