News
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyWar arose recently, anthropologists contend
Infrequent killings among hunter-gatherer groups fit a scenario of a largely peaceful Stone Age, a study concludes.
By Bruce Bower -
 Tech
TechSurgical tool smokes out cancer in seconds
Sniffing for telltale molecules, method analyzes tissue with every cut.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsTechnique inactivates Down-causing chromosome
Though far from a cure, the advance could eventually lead to gene therapy that alleviates some symptoms.
-
 Animals
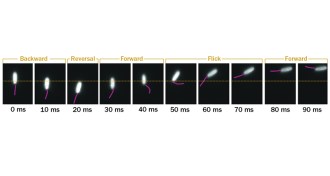
AnimalsFattened livers prep white sharks for extreme migrations
The organ's reserves enable a long journey from waters off California to Hawaii and back, tracking data suggest.
By Susan Milius -
-
 Life
LifeGenetic test fingers viral, bacterial infections
If made to take less time, test could help doctors treat children's fevers.
-
 Tech
TechSound waves put levitation on the move
Technique transports nonmagnetic particles such as cells, water droplets and coffee grounds.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsSponges boom thanks to Antarctic ice shelf bust
Previously thought to grow at a slow pace, the sea creatures exploded in number.
-
 Earth
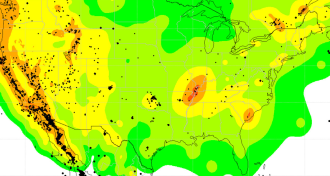
EarthHuge quakes may foretell smaller, human-caused ones
Distant powerful temblors triggered ominous activity at wastewater injection sites.
By Erin Wayman -
 Life
LifeGene therapy treats children with rare diseases
Six kids are healthy, up to three years after treatment.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryCoatings have simple recipe for success
Chemists encapsulate tiny objects using natural ingredients and easy, inexpensive process.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat and when babies first eat may affect diabetes risk
Children at risk of type 1 diabetes are better off waiting until 4 months of age to consume solid foods.
By Nathan Seppa