Uncategorized
-
 Climate
ClimateThere’s something cool about Arctic bird poop
Ammonia from seabird poop helps brighten clouds in the Arctic, slightly cooling the region’s climate.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceInfant brains have powerful reactions to fear
Babies can recognize facial emotions, especially fear, as early as 5 months old.
-
 Life
LifeLichens are an early warning system for forest health
Lichens, fascinating mosaics of fungi and algae or cyanobacteria, are made for sensing environmental change.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMarijuana use weakens heart muscle
Marijuana linked to dangerous heart stress.
By Laura Beil -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceZap to the head leads to fat loss
Stimulating the vestibular nerve led people to shed fat in a small trial.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyInteractive map reveals hidden details of the Milky Way
Gleamoscope, an interactive map, lets you explore the Milky Way galaxy and the nearby universe in many different electromagnetic frequencies.
-
 Health & Medicine
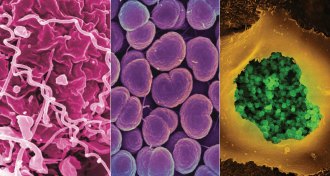
Health & MedicineCDC sounds alarm on STDs
The combined reported cases of three common sexually transmitted diseases reached a historic peak in 2015, a new CDC report says.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsNew analysis boosts case for smaller proton
Electron scattering data hint at a slightly smaller proton radius.
-
 Health & Medicine
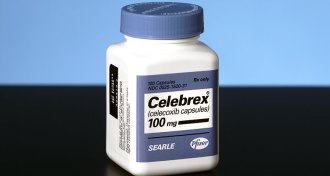
Health & MedicinePopular painkiller doesn’t have more heart risks than others, study claims
A long anticipated trial of the drug Celebrex finds it poses no more risk to the heart than do similar painkillers, but critics cite flaws in the study.
By Laura Beil -
 Life
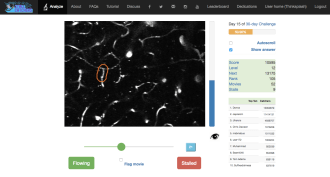
LifeWebsite turns Alzheimer’s research into a game
A new game assists Alzheimer’s researchers in the hunt for stalled blood vessels in the brains of mice.
-
 Physics
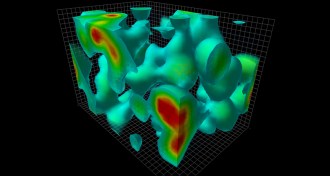
Physics‘Void’ dives into physics of nothingness
In modern physics, emptiness is elusive and difficult to define, a new book shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNarwhals are really, really good at echolocation
Audio recordings from the Arctic suggest that narwhals take directional sonar to the extreme.