Uncategorized
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAI helps archaeologists solve a Roman gaming mystery
Researchers used AI-driven virtual players to test more than 100 rule sets, matching gameplay to wear patterns on a Roman limestone board.
By Tom Metcalfe -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDaily cups of caffeinated coffee or mugs of tea may lower dementia risk
A long-term observational study found a link between the amount of tea and caffeinated coffee people drank and the risk of dementia.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThe world’s oldest piece of clothing might be an Ice Age–era hide from Oregon
Two pieces of elk hide connected by a twisted-fiber cord are the earliest evidence of sewing. But what they were used for is still a mystery.
By Tom Metcalfe -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyAutistic Barbie reminds us stories have the power to counter misinformation
Representation and rigorous science compete with the Trump administration’s false claims about autism.
-
 Physics
PhysicsThe only U.S. particle collider shuts down – so a new one may rise
The famed collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory has ended operations, but if all goes to plan, a new collider will rise from its ashes.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyWhen the fish stop biting, ice fishers follow the crowd
Study showcases how modern-day foragers stick together when seeking food. Such social forces could help explain the emergence of complex thinking.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Animals
AnimalsA bonobo’s imaginary tea party suggests apes can play pretend
Apes, like humans, are capable of pretend play, challenging long-held views about how animals think, a new study suggests.
By RJ Mackenzie -
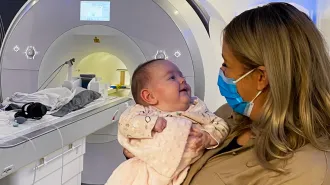 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBabies brains’ can follow a beat as soon as they’re born
Brain scans and signals show babies can sort images and sense rhythm, offering new insight into how infant brains are wired from the start.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe best way to help Alzheimer’s patients may be to help their caregivers
A mathematical model simulated patient outcomes when given caregiver support or an expensive Alzheimer’s drug to determine cost and health benefits.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGum disease bacteria can promote cancer growth in mice
In mice, the oral bacteria F. nucleatum can travel to mammary tissue via the bloodstream, where it can damage healthy cells.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsSome dung beetles dig deep to keep their eggs cool
A temperate tunneling species of dung beetle seems capable of adapting to climate change, but their tropical cousins may be less resilient.
-
 Space
SpaceArtemis II is returning humans to the moon with science riding shotgun
NASA’s Artemis II could be the first time human eyes set sight on the farside of the moon — and there are things human eyes can see that cameras can’t.