Uncategorized
-
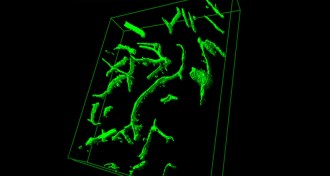 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYoung blood proven good for old brain
Blood — or one of its protein components — restores some of youth’s vibrancy to elderly mouse brains.
-
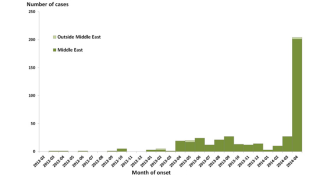 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMERS outbreak picks up pace in Middle East
As the number of MERS cases increases, researchers race to learn more about the deadly virus carried by camels.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologySee the sky in a different light
An interactive map lets you explore the galaxy with infrared light.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNarwhal has the strangest tooth in the sea
Sometimes called the unicorn of the sea, the male narwhal’s tusk is actually a tooth. Narwhals detect changes in water salinity using only these tusks, a new study finds.
By Susan Milius -
 Physics
PhysicsGravity’s Ghost and Big Dog
Sociologist Harry Collins chronicles the occasionally heated (and often arcane) debates among scientists studying gravitational waves.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyIlluminating a dark universe
The film "Dark Universe" compresses a century of discovery into a crisp, comprehensible half hour.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow to milk a naked mole-rat
For the sake of science, Olav Oftedal has milked bats, bears and a lot of other mammals. But a naked mole-rat was something new.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFirst MERS case found in the U.S.
Patient in Indiana had traveled from Arabian Peninsula, where most of the 463 cases of Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome have occurred.
-

-

Prying tales from ancient DNA and a far-away moon
Exploring the DNA of ancient bones on Earth and the waters of an icy moon, Europa, could shift our views of life.
By Eva Emerson -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyWritten in bone
Researchers are reconstructing the migrations that carried agriculture into Europe by analyzing DNA from the skeletons of early farmers and the people they displaced.
-
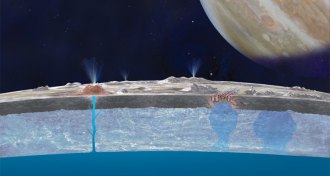 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe ice of a distant moon
Jupiter’s moon Europa hides a liquid ocean, and conceivably life, under kilometers of ice. The challenge for engineers is how to penetrate that frozen barrier with technology that can be launched into space and operated remotely.
By Meghan Rosen