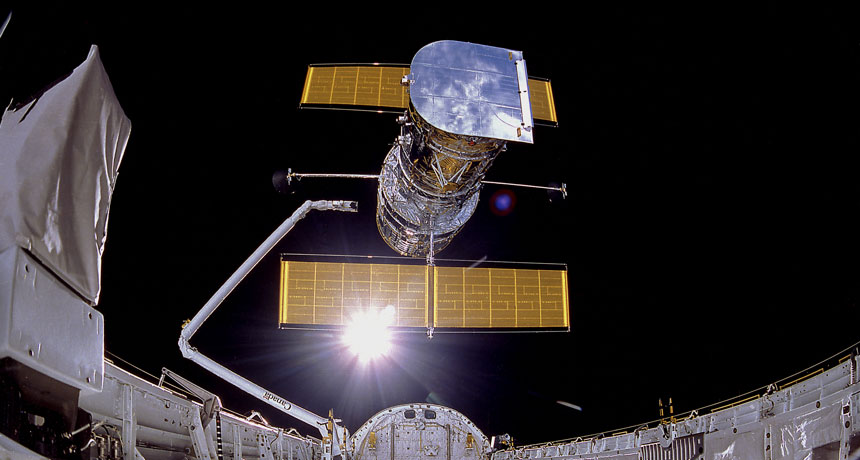
A SPACE TELESCOPE IS BORN From the start, the Hubble Space Telescope (seen being released from the cargo bay of the space shuttle Discovery on April 25, 1990) has survived many potentially career-ending scares.
NASA
Hubble’s in trouble again.
The 28-year-old space telescope, in orbit around the Earth, put itself to sleep on October 5 because of an undiagnosed problem with one of its steering wheels. But once more, astronomers are optimistic about Hubble’s chances of recovery. After all, it’s just the latest nail-biting moment in the history of a telescope that has defied all life-expectancy predictions.
There is one major difference this time. Hubble was designed to be repaired by astronauts on the space shuttle. Each time the telescope broke previously, a shuttle mission fixed it. “That we can’t do anymore, because there ain’t no shuttle,” says astronomer Helmut Jenkner of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, who is Hubble’s deputy mission head.
The most recent problem started when one of the three gyroscopes that control where the telescope points failed. That wasn’t surprising, says Hubble senior project scientist Jennifer Wiseman of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. That particular gyroscope had been glitching for about a year. But when the team turned on a backup gyroscope, it didn’t function properly either.
Astronomers are working to figure out what went wrong and how to fix it from the ground. The mood is upbeat, Wiseman says. But even if the gyroscope doesn’t come back online, there are ways to point Hubble and continue observing with as few as one gyroscope.
“This is not a catastrophic failure, but it is a sign of mortality,” says astronomer Robert Kirshner of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Mass. Like cataracts, he says, it’s “a sign of aging, but there’s a very good remedy.”
While we wait for news of how Hubble is faring, here’s a look back at some of its previous hiccups and repair missions.
1990: The blurry mirror
On June 27, 1990, three months after the space telescope launched, astronomers discovered an aberration in Hubble’s primary mirror. Its curvature was off by two micrometers, making the images slightly blurry.
The telescope soldiered on, despite being the butt of jokes on late-night TV. It observed a supernova that exploded in 1987 (SN: 2/18/17, p. 20), measured the distance to a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way and took its first look at Jupiter before the space shuttle Endeavour arrived to fix the mirror in December 1993.
1999: The first gyroscope crisis

An already planned preventative maintenance shuttle mission suddenly became more urgent. NASA split the mission into two parts to get to the telescope more quickly. The first part became a rescue mission: Astronauts flew the space shuttle Discovery to Hubble that December to install all new gyroscopes and a new computer.
2004: Final shuttle mission canceled
After the space shuttle Columbia disintegrated while re-entering Earth’s atmosphere in 2003, NASA canceled the planned fifth and final Hubble reservicing mission. “That could really have been the beginning of the end,” Jenkner says.
The team has known for more than a decade that someday Hubble will have to work with fewer than three gyroscopes. To prepare, Hubble’s operations team deliberately shut down one of the telescope’s gyroscopes in 2005, to observe with only two.
“We’ve been thinking about this possibility for many years,” Wiseman says. “This time will come at some point in Hubble’s mission, either now or later.”
Shutting down the third gyroscope was expected to extend Hubble’s life by only eight months, until mid-2008. In the meantime, two of the telescope’s scientific instruments — the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph and the Advanced Camera for Surveys — stopped working due to power supply failures.
Good as new
Space shuttle missions returned five times to Hubble over the space telescope’s first 19 years to repair it. In 2002, astronauts aboard the space shuttle Columbia visited Hubble to replace its solar panels and install new cameras (seen here inside Columbia’s cargo bay with the glow of Earth’s horizon in the background). The tragic destruction of Columbia in 2003 almost made this the last Hubble visit.
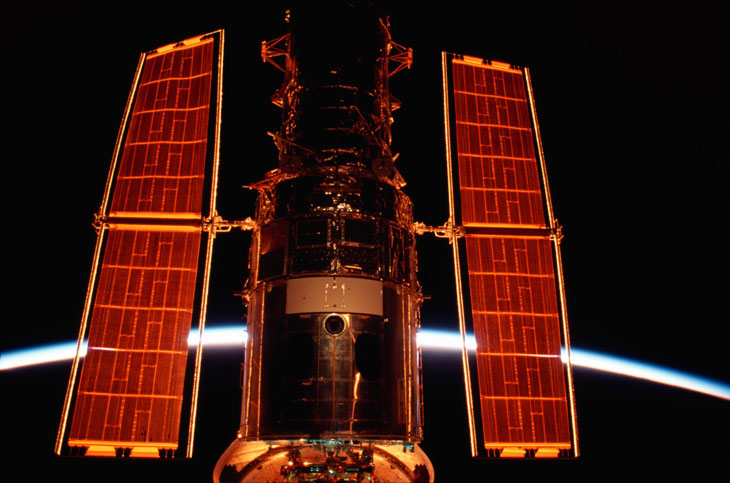
2009: New lease on life
Fortunately, NASA restored the final servicing mission, and the space shuttle Atlantis visited Hubble in May 2009 (SN Online: 5/11/09). That mission restored Hubble’s cameras, installed new ones and crucially, left the space telescope with six new gyroscopes, three for immediate use and three backups. The three gyroscopes still in operation (including the backup that is currently malfunctioning) are of a newer type, and are expected to live five times as long as the older ones, which last four to six years.
The team expects Hubble to continue doing science well into the 2020s and to have years of overlap with its successor, the James Webb Space Telescope, due to launch in 2021. “We are always worried,” says Jenkner, who has been working on Hubble since 1983. “At the same time, we are confident that we will be running for quite some time more.”