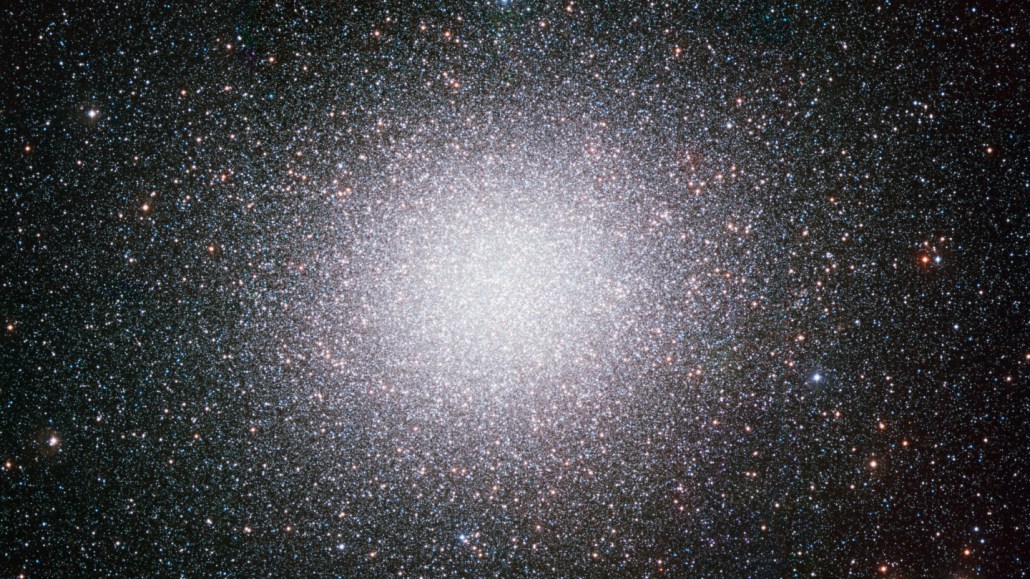
Visible to the naked eye under a dark sky, Omega Centauri is one of our galaxy’s most luminous star clusters, boasting millions of old stars — but no evidence for a previously reported intermediate-mass black hole, according to a new study.
ESO
Contrary to a previous report, there’s no evidence of an intermediate-mass black hole in Omega Centauri, the Milky Way’s most massive and luminous globular star cluster, a new study finds. Instead, a hive of much smaller black holes diving into and out of the tightly packed star cluster’s center can explain the movement and distribution of its many ancient stars.
“What we found in our analysis is that the data favor an extended component [of stellar-mass black holes] as opposed to an intermediate-mass black hole,” says Andrés Bañares-Hernández, an astronomer at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias in La Laguna, Spain. Some 10,000 to 20,000 stellar-mass black holes — adding up to between 200,000 and 300,000 times the mass of the sun — that are spread around the center of the star cluster can explain the observations, he says.
The study doesn’t completely rule out an intermediate-mass black hole, but if one is there, it’s much smaller than previously suggested. No black hole heftier than 6,000 times the mass of the sun exists in the star cluster, his team concludes in work submitted August 1 to arXiv.org.
In contrast, the other research team said that seven stars near this cluster’s center are moving so fast they must be whirling around a black hole of between 8,200 and 50,000 solar masses (SN: 7/10/24). Astronomers have long sought these middleweight black holes because if the elusive objects truly exist, they could help explain black hole evolution.
In the new work, Bañares-Hernández and his colleagues studied the motions of not only ordinary stars in Omega Centauri but also five of its millisecond pulsars. Spinning at more than a hundred times a second, a millisecond pulsar emits a radio pulse toward us each time the star turns (SN: 7/22/22). If the pulsar is moving toward Earth, each pulse takes less time to reach us. Precise timing of these pulses therefore reveals the pulsar’s exact velocity and acceleration toward or away from Earth, which helped the astronomers determine how mass is distributed throughout the star cluster.
“It’s probably one of the best methods to use, because the millisecond pulsars are very stable, and they do give you a very clear signal of what’s going on,” says Simon Portegies Zwart, an astronomer at Leiden Observatory in the Netherlands who was not part of either research team.
The astronomer who led that study declined to comment on the new work until it has been accepted for publication, but he stands by his original conclusion. “We think that the best explanation for these very fast-moving stars being so close to the center of Omega Centauri is that they are bound by an intermediate-mass black hole,” says Maximilian Häberle of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Heidelberg, Germany.
Astronomers unaffiliated with either research team are split in their verdict. “I don’t think there’s any robust evidence for an intermediate-mass black hole,” says Gerry Gilmore, an astronomer at the University of Cambridge. “In the new study, they have done a much better job than anyone has before of including the types of [dim] stellar populations that we know for a fact are very, very common” at the centers of globular clusters: neutron stars and stellar-mass black holes.
On the other hand, astronomer Daryl Haggard of McGill University in Montreal calls evidence for the middleweight black hole “pretty compelling. It’s very, very, very hard to come up with a model that gets those fast-moving stars into the center of Omega Centauri and have them not guided by an intermediate-mass black hole.”
How to resolve the controversy? “Get me an orbit,” says Portegies Zwart, who states that he’s “a little bit skeptical” of the existence of the intermediate-mass black hole. A star orbiting something invisible that weighs thousands of solar masses would be solid proof, he says. So would a glow from gas falling into the black hole, Haggard says.