In his dialogue Timaeus, the Greek philosopher Plato (427–347 B.C.) carefully laid out his reasoning for ascribing certain geometric shapes to the minuscule particles that constituted the four elements of matter. In his view, these elements–fire, air, water, and earth–were all aggregates of tiny solids, each one having the shape of one of the regular polyhedra.
As the lightest and sharpest of the elements, fire was a tetrahedron. As the most stable, earth consisted of cubes. Water was an icosahedron, and air had to be an octahedron. The universe itself was a perfect sphere.
The fifth regular solid–the dodecahedron–was barely mentioned. Plato merely noted vaguely that “as there is still one construction left, the fifth, God made use of it for the universe when he painted it.”
Plato was probably thinking of an earlier tradition dating back to the Pythagoreans–the notion that the dodecahedron formed the “timbers” on which the spherical bulk of the heavens was built. Indeed, the structure of the world was sometimes compared to that of building a ship, where the keel and ribs would be laid out first.
Curiously, in the earlier Phaedo, Plato described the earth itself, when viewed from above, as “many-colored like the balls that are made of twelve pieces of leather.”
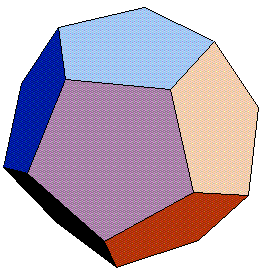
The dodecahedron has 12 faces (a number associated with the zodiac) and 30 edges. All the faces are identical, regular pentagons. It also has 20 corners, or vertices–each one a point where three edges or three faces meet.
This Platonic solid has been an object of fascination for millennia. Archaeologists have unearthed models of dodecahedra at several sites in Europe, including a dodecahedral model in Germany that had holes of different sizes punctuing its faces.
Leonardo da Vinci made exquisitely careful drawings of dodecahedra and other polyhedra (see http://www.georgehart.com/virtual-polyhedra/leonardo.html). A portrait by Jacopo de’ Barbari (1440–1516) showing Luca Pacioli (1445–1514), a mathematician who used Leonardo’s drawings to illustrate his own writings, featured a dodecahedron perched atop a copy of Euclid’s Elements (see http://www.georgehart.com/virtual-polyhedra/pacioli.html). Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) placed a dodecahedron between Mars and Jupiter in his ingenious model of the solar system and later studied the properties of polyhedra in considerable detail (see http://www.georgehart.com/virtual-polyhedra/kepler.html).
In modern times, the Spanish painter Salvador Dalí (1904–1989) echoed Pythagorean mysticism when he hung a dodecahedron in the background of his 1955 painting “The Sacrament of the Last Supper” (see http://www.ellensplace.net/dali.html.
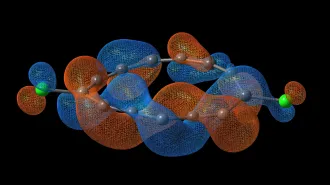
Now, the dodecahedron is in the news again. A team of chemists from Germany and the United States has fashioned one out of carbon atoms to form the molecule C20. Horst Prinzbach of Albert Ludwigs University in Freiburg, Germany, and his coworkers report their feat in the Sept. 7 Nature.
This newly synthesized molecule is the smallest member of the family of closed-cage carbon molecules known as fullerenes. All fullerenes incorporate exactly 12 pentagonal rings of carbon atoms, with some number of hexagonal rings filling in the rest of the structure. The most famous is buckminsterfullerene, discovered in 1985, which is made up of 60 carbon atoms arranged in 12 pentagonal rings and 20 hexagonal rings. It has the shape of a truncated icosahedron–the same configuration seen on a soccer ball.
The existence of dodecahedral C20 is a bit of a surprise, however. Theorists had thought that the absence of hexagonal rings would mean that the bonds between carbon atoms would be under too much strain because of the miniball’s high curvature for the molecule to hold together. Some sets of calculations had showed that a bowl would be more stable than a cage configuration, and previous experiments had produced only chains and rings of carbon atoms.
Prinzbach and his collaborators started with a molecule known as dodecahedrane, C20H20. First synthesized in 1982, this molecule consists of a roughly spherical cage of carbon atoms, each one capped with a hydrogen atom. The chemists replaced the hydrogen atoms with less clingy bromine atoms, then stripped away the bromine, leaving a delicate, dodecahedral cage of pure carbon.
Though the molecule doesn’t last very long, it now has a place in Plato’s universe.